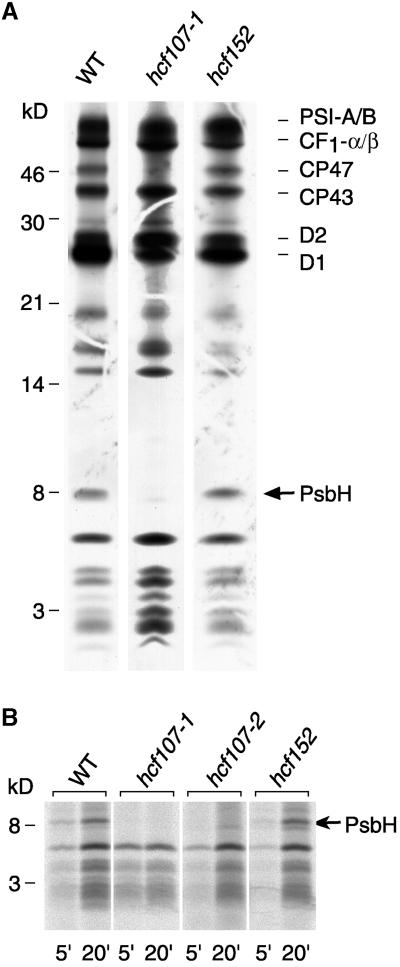
Figure 2.
In Vivo Protein Synthesis of Plastome-Encoded Membrane Proteins of hcf107-1, hcf107-2, hcf152, and Wild-Type (WT) Plants.
(A) Pulse labeling for 15 min. Wild-type and mutant proteins with equivalent amounts of radioactivity (100,000 cpm) were separated electrophoretically on a 12.5% polyacrylamide-SDS/urea gel (Schägger and von Jagow, 1987), blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane, and analyzed by fluorography. The position of the PsbH subunit of PSII is indicated. CF1-α/β, α and β subunits of the chloroplast ATP synthase; WT, wild type.
(B) Kinetics of 35S incorporation into the 8-kD protein. The labeling periods were 5 min (5′) and 20 min (20′). Only the lower part of the polyacrylamide-SDS/urea gel is shown. The gel was loaded with the following amounts of protein and radioactivity: WT, 5 μg of protein (5′, 20,000 cpm; 20′, 80,000 cpm); hcf107-1, 10 μg of protein (5′, 25,000 cpm; 20′, 40,000 cpm); hcf107-2, 15 μg of protein (5′, 20,000 cpm; 20′, 60,000 cpm); and hcf152, 15 μg of protein (5′, 20,000 cpm; 20′, 90,000 cpm). Radiolabeled proteins were detected by phosphorimaging.