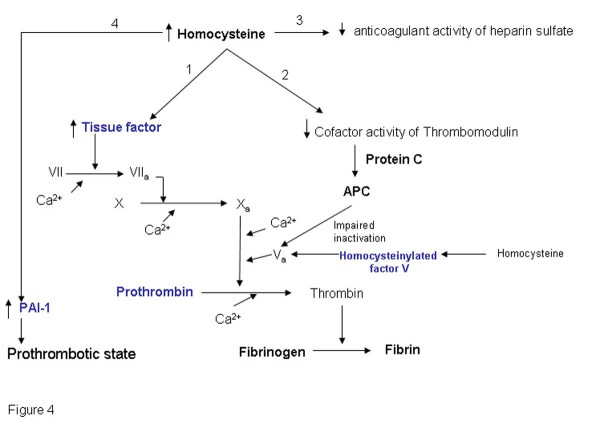
Figure 4.
Elevated homocysteine levels and the Coagulation pathway. Elevated homocysteine levels may lead to thrombosis either by increasing the activity of the tissue factor (branch 1) thereby facilitating the coagulation cascade or by inhibiting the anticoagulant pathways (branch 2 and 3). The genes marked in blue have been identified by literature based searches as mentioned in the methods section. The solid and dotted lines indicate direct and indirect (multi step) interaction/ conversion respectively.