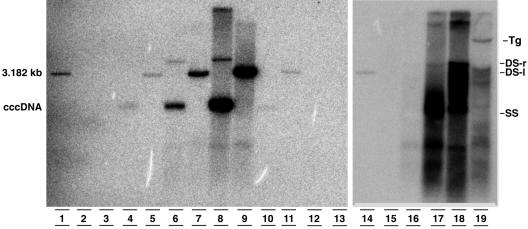
FIG. 7.
Southern blot analysis of HBV cccDNA (lanes 2 to 13) and replicative intermediates (lanes 15 to 19) isolated from the livers of a noninfected chimeric mouse (lanes 2, 3, and 15), short-term (lanes 4, 5, and 16) and long-term (lanes 6, 7, and 17) HBV-infected uPA-SCID mice, a patient with HBV-induced FCH (lanes 8, 9, and 18), a chronically HBV-infected chimpanzee (lanes 10 and 11), and an HBV-infected transgenic mouse (lanes 12, 13, and 19). A 3.182-kb molecular weight marker is also included (lanes 1 and 14). After EcoRI digestion, the cccDNA molecules linearized to a double-stranded, linear (DS-l) form (lanes 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, and 13). As expected, cccDNA is not detectable in the HBV transgenic (Tg) mouse extracts. The relative amounts of cccDNA between the different samples cannot be compared because of the varying sizes of the starting material. Replicative intermediates can be easily visualized in the long-term mouse liver but are hardly detectable in the short-term-infected chimeric mouse.