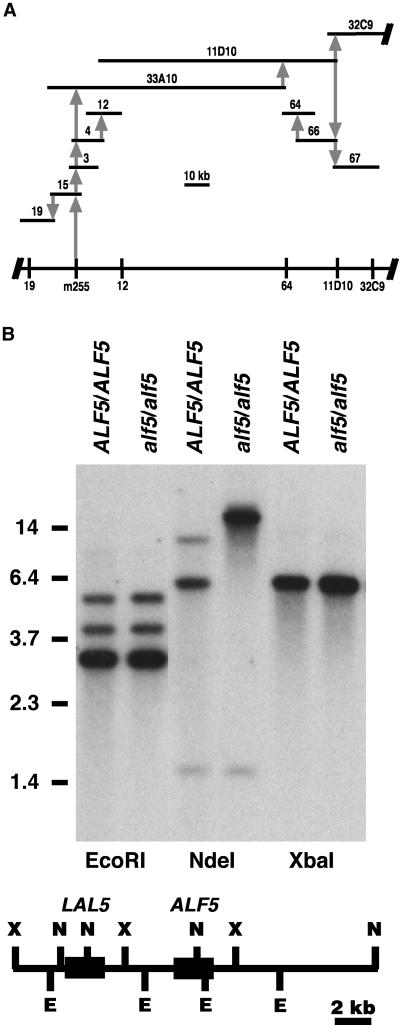
Figure 3.
Positional Cloning of alf5.
(A) Physical genomic map of the alf5 region. The span of each Arabidopsis genomic clone (horizontal bars) is proportional to the 10-kb scale, and its position is relative to its genome coverage. Clones 33A10, 11D10, and 32C9 are Texas A&M University BACs; clones 3, 4, 12, 15, 19, 64, 66, or 67 are from λ libraries. The positions of CAPS makers (λ19, m255, λ12, λ64, 11D10, and 32C9) along chromosome 3 are depicted at the bottom. The initial association of each cloned segment to the contig is represented by a gray vertical arrow: the sequence used as a hybridization probe is the base of the arrow, and the sequence identified by the hybridization probe is at the arrow point.
(B) ALF5 and alf5 genomic DNA. Genomic DNA of ALF5 and alf5 plant lines was digested with the restriction enzymes EcoRI, NdeI, and XbaI. The DNA gel blot was hybridized to the ALF5 cDNA. The mobilities of standard restriction fragments are indicated at left with their sizes in kb. At bottom, the expected restriction map was compiled from the BAC MDB19 genomic sequence. E, EcoRI; N, NdeI; X, XbaI. Black boxes represent the ALF5 and LAL5 coding regions.