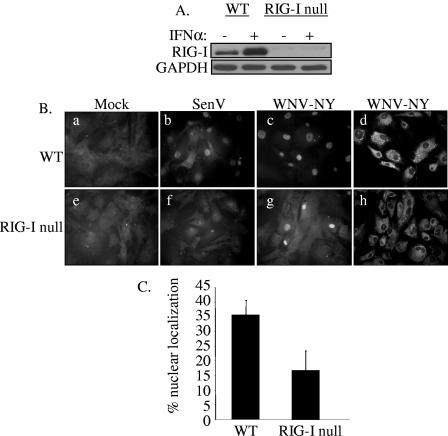
FIG. 6.
IRF-3 localization in WNV-NY-infected WT and RIG-I null MEFs. (A) The RIG-I null genotype was confirmed by immunoblot analysis of lysates prepared from WT and IRF-3 null MEFs incubated in the presence or absence of 200 U/ml mouse IFN-α. Steady-state levels of RIG-I were assessed using a rabbit polyclonal antiserum to RIG-I. (B) Cellular localization of IRF-3 in WT (a to c) and RIG-I null (e to g) MEFs was examined. Mock- (a and e), SenV- (b and f), and WNV-NY- (c and g) infected cells were probed for IRF-3 using an IRF-3 polyclonal antiserum and an Alexa 488-conjugated secondary antibody (a through c and e through g). WNV protein expression (d and h) was detected using a mouse polyclonal anti-WNV antibody and rhodamine-conjugated secondary antibody. (C) Percent IRF-3 nuclear localization in WNV-NY-infected WT and RIG-I null MEFs. The number of cells with nuclear IRF-3 was divided by the total number of cells present in nine individual fields of WT and RIG-I null MEFs.