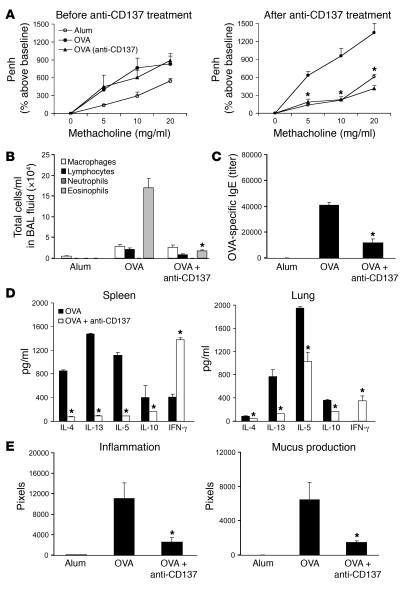
Figure 4. Therapeutic effect of anti-CD137 mAb in a chronic asthma model.
BALB/c mice were immunized with OVA on day 1 and challenged with OVA several times intranasally during the following 31 days. Lung function was measured on day 32. Anti-CD137 mAb was injected the same day, followed by further intranasal challenges with OVA (days 39–41). (A) OVA immunization resulted in methacholine-induced AHR as measured 1 day after the last intranasal OVA challenge (day 32). Injection of anti-CD137 mAb 12 hours after the first AHR measurement completely inhibited this already established AHR as demonstrated 10 days later. (B) Mice were sacrificed on day 43, and BAL was performed. Anti-CD137 mAb almost completely abrogated the total cell number in the BAL fluid of OVA-immunized BALB/c mice. (C) Anti-CD137 mAb reduced OVA-specific IgE serum levels in OVA-immunized BALB/c mice. (D) Anti-CD137 mAb converted an established Th2 to a Th1 cytokine response in culture supernatants of splenocytes and lung cells in OVA-immunized BALB/c mice. (E) Quantification of lung inflammation and mucus production by a computer-based image-analyzing program clearly demonstrated the inhibitory effect of anti-CD137 mAb. *P < 0.05, OVA plus anti-CD137 mAb versus OVA plus control antibody by Student’s t test. (a, b, and e) n ≥ 8 animals per group and data point; data are expressed as mean ± SEM from 2 independent experiments. (c and d) n ≥ 4 animals for each group; here representative results from 1 of 2 experiments a shown.