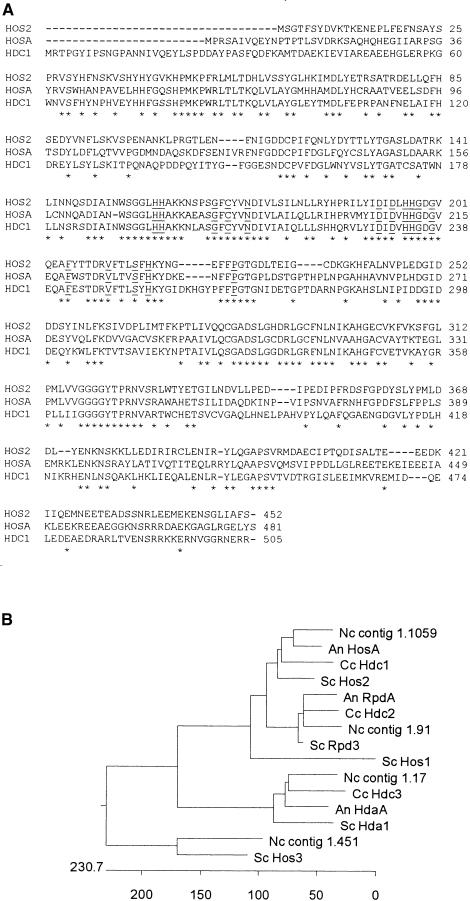
Figure 1.
Alignment of the Predicted Amino Acid Sequences of HDC1 and Related Genes.
(A) Proteins shown are the products of HOS2 of S. cerevisiae (Rundlett et al., 1996; SWISS-PROT accession number P53096), HOSA of A. nidulans (Graessle et al., 2000; GenBank accession number AF164342), and HDC1 of C. carbonum (GenBank accession number AF306507) using CLUSTAL W (Thompson et al., 1994). Amino acids that are identical in all three proteins are indicated by asterisks. Sixteen of the 17 amino acids that are highly conserved in all RPD3-like HDAs and related bacterial proteins are underlined (Hassig et al., 1998).
(B) Unrooted cladogram showing relatedness of HDAC proteins. HosA and RpdA are from A. nidulans (An; Graessle et al., 2000). Hda1, Rpd3, Hos1, Hos2, and Hos3 are from S. cerevisiae (SC; Vidal and Gaber, 1991; Rundlett et al., 1996). Hdc1, Hdc2, and Hdc3 are from C. carbonum (Cc; this article; D. Baidyaroy and J.D. Walton, unpublished data; E-M. Brandtner, S. Graessle, and G. Brosch, unpublished data). Contigs 1.1059, 1.91, 1.17, and 1.451 represent predicted proteins from the eponymous genomic DNA sequences of N. crassa (Nc; http://www.genome.wi.mit.edu/annotation/fungi/neurospora/). The units on the scale at bottom are numbers of substitution events.