Abstract
1. Rates of oxygen uptake and of anaerobic glycolysis were estimated in slices from the renal cortex and medulla (a) of adult rats and guinea-pigs, (b) of new-born (1-, 5- and 21-day-old) rats and of guinea-pigs of 1, 12, 21, 24 and 120 hr age.
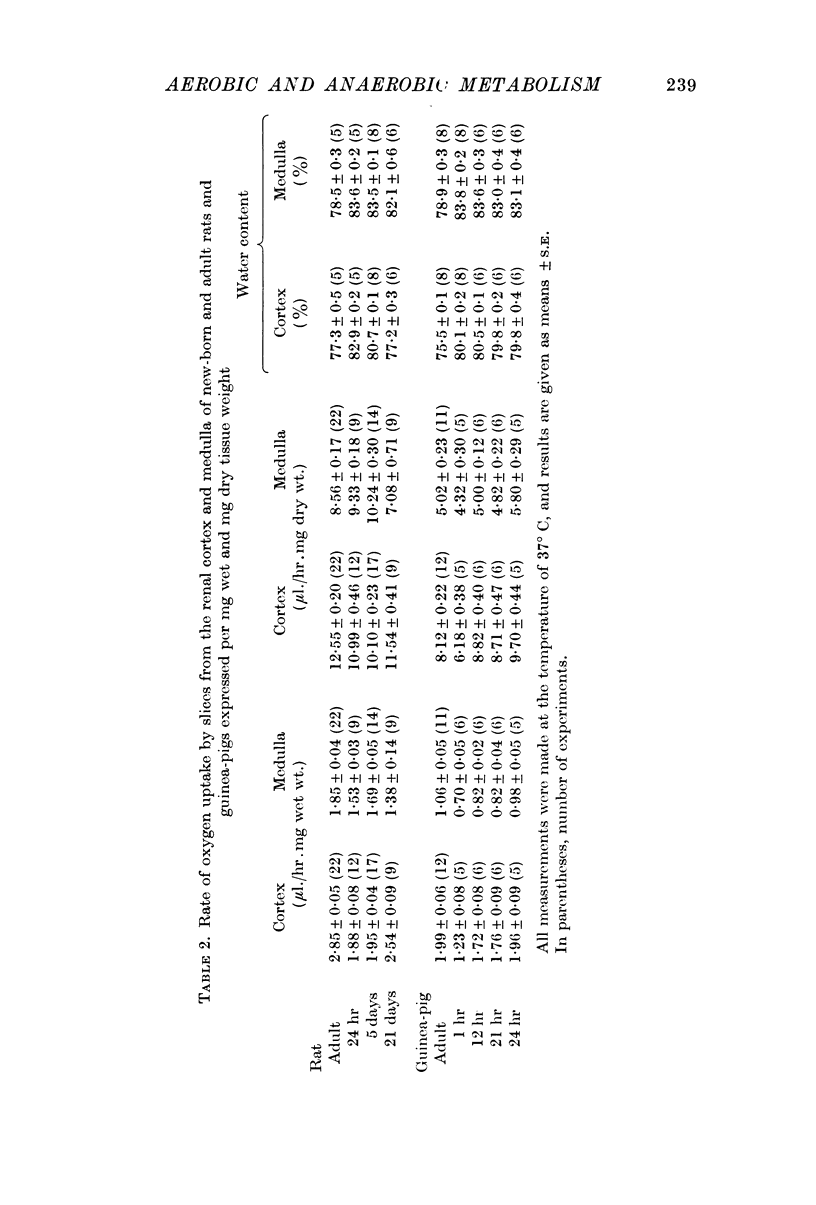
2. In the adult rat, QO2 values for the cortex were 12·55 ± 0·20 (22) and for the medulla: 8·56 ± 0·17 (22) μl./hr.mg dry weight, while in the new-born rat (24 hr old) they were 10·99 ± 0·46 (12) and 9·33 ± 0·18 (9) μl./hr.mg dry weight respectively.
3. Values for QCO2N2 (anaerobic glycolysis) in the 14 hr old new-born rat were in the renal cortex 9·65 ± 0·35 (5) and in the medulla 7·39 ± 0·43 (5) μl./hr.mg dry weight; while in the adult they were 2·25 ± 0·08 (16) and 5·76 ± 0·14 (16) μl./hr.mg dry weight, respectively.
4. In the adult guinea-pig values for QCO2N2 were of the same order as in the adult rat, though the rate of O2 uptake was for the cortex 8·12 ± 0·22 (12) and for the medulla 5·02 ± 0·23 (11) μl./hr.mg dry weight.
5. Though the QO2 values in the renal cortex and medulla were smaller in the 1 hr old new-born guinea-pig, they were already increasing in the 12 hr old neonate.
6. The results are discussed in the light of enzyme changes occurring during the process of maturation of the nephron as indicated by histochemical observations.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogomolova N. A. Vozrastnye izmeneniia pochki beloi krysy. Arkh Anat Gistol Embriol. 1965 Apr;48(4):80–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKER S. E., HELLER H. The mechanism of water diuresis in adult and newborn guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1951 Jan;112(1-2):149–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker S. E., Shirley D. G. Rate of oxygen uptake and glycolysis in kidneys of adult and new-born rats and guinea-pigs, in vitro. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):67P–68P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance R. A., Stanier M. W. The function of the metanephros of foetal rabbits and pigs. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151(3):479–483. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance R. A., Young W. F. The secretion of urine by newborn infants. J Physiol. 1941 Mar 25;99(3):265–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1941.sp003900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON J. R. Osmoregulation in surviving slices from the kidneys of adult rats. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1950 Oct 13;137(888):378–402. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1950.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. R. Some effects of glucose and calcium upon the metabolism of kidney slices from adult and newborn rats. Biochem J. 1949;45(1):68–74. doi: 10.1042/bj0450068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WACHSTEIN M., BRADSHAW M. HISTOCHEMICAL LOCALIZATION OF ENZYME ACTIVITY IN THE KIDNEYS OF THREE MAMMALIAN SPECIES DURING THEIR POSTNATAL DEVELOPMENT. J Histochem Cytochem. 1965 Jan;13:44–56. doi: 10.1177/13.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAM R., DAVIES R. E. Energy requirements for ion transport in steady-state systems. Nature. 1954 Mar 13;173(4402):494–494. doi: 10.1038/173494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAM R. Metabolic changes in rabbit kidney cortex during the first few weeks after birth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Dec 23;54:574–576. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAM R. Sodium and potassium movements in kidney cortex slices from new-born animals. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:358–369. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WU R. RATE-LIMITING FACTORS IN GLYCOLYSIS AND INORGANIC ORTHOPHOSPHATE TRANSPORT IN RAT LIVER AND KIDNEY SLICES. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2373–2381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


