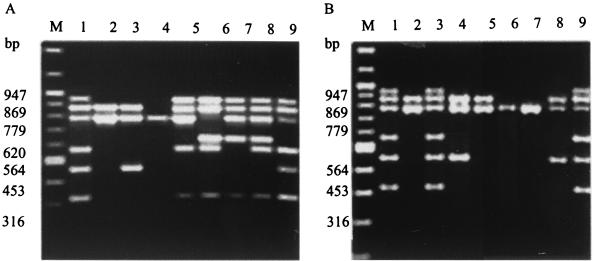
FIG. 1.
(A) Ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel electrophoresis of hexaplex PCR products from Vibrio cholerae strains. Lane M, 100-bp DNA ladder (NEB); lanes 1, 8 and 9, cholera toxin-producing V. cholerae O1 El Tor strain 20, classical strain 569B, and V. cholerae O139 strain ATCC 51394, respectively; lanes 2 through 4, non-cholera toxin-producing V. cholerae O1 El Tor strains X392, 274-80, and 1074-78, respectively; lane 5, tcpA-negative V. cholerae O1 classical strain O395 RT 110-12; lane 6, toxR-negative V. cholerae O1 classical strain O395-12; lane 7, ctxA-negative V. cholerae O1 classical strain CVD 103-HgR. (B) Hexaplex PCR products of representative V. cholerae O1, O139, non-O1, and non-O139 and V. mimicus strains in an ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel. Lane M, 100-bp DNA ladder (NEB); lane 1, cholera toxin-producing V. cholerae O1 El Tor strain KO63 (diarrhea isolate from Kerala, India, 2000); lane 2, non-cholera toxin-producing V. cholerae O1 El Tor strain GS2 (isolate from Gerris spinolae, Varanasi, India, 1987); lane 3, cholera toxin-producing V. cholerae O139 strain VO522 (diarrhea isolate from Varanasi, India, 1994); lane 4, non-cholera toxin-producing V. cholerae O139 strain CO788 (diarrhea isolate from Kolkata, India, 1992); lanes 5 and 6, non-cholera toxin-producing V. cholerae non-O1, non-O139 strains 12475 and 13094, respectively (diarrhea isolates from Varanasi, India, 1979); lanes 7 and 8, non-cholera toxin-producing V. mimicus strains WM18 (water isolate from the River Ganges, Varanasi, India, 1988) and VM2 (water isolate from the River Ganges, Varanasi, India, 1988), respectively; and lane 9, cholera toxin-producing V. mimicus strain WM8 (water isolate from the River Ganges, Varanasi, India, 1986).