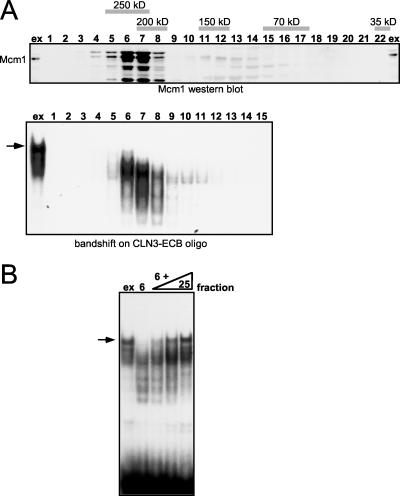
FIG. 6.
Gel filtration analysis of ECB binding complexes. (A) Clarified yeast crude extracts were subjected to gel filtration on a Sephacryl S200 column. Fractions were collected and assayed by Western blotting for the presence of Mcm1 (upper panel) and by gel retardation assays for ECB binding activity (lower panel). The first lane contains the extract (ex) loaded onto the column. Numbers indicate fractions, and gray bars depict the elution position of marker proteins run in parallel. The band shift assay below shows the only fractions in which DNA binding complexes were detected. The arrow marks the ECB-specific complex formed from crude yeast cell extracts. (B) Reconstitution of the ECB-specific complex. The CLN3-ECB oligonucleotide was incubated with crude extract, fraction 6 of the gel filtration, or a combination of fraction 6 and later fractions from the same column. Addition of increasing amounts of fraction 25 (three right lanes) restored the complex to a position comparable to that obtained with crude cell extracts, denoted by the arrow.