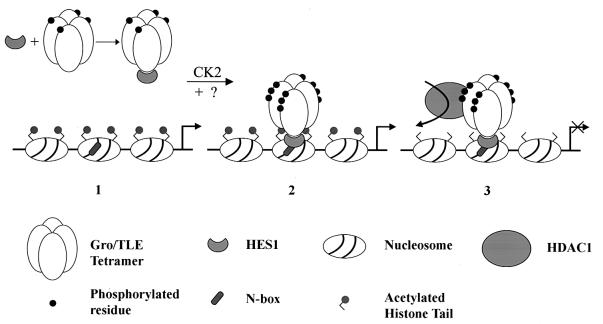
FIG. 8.
Proposed model for transcriptional repression mediated by Hes1 and Gro/TLEs. (Structures 1 and 2) The interaction of Hes1 with oligomeric Gro/TLE leads to hyperphosphorylation of the latter via a mechanism involving protein kinase CK2 and perhaps other as-yet-unidentified kinases. Hes1 then targets hyperphosphorylated Gro/TLE to specific DNA sequences (N boxes), where additional phosphorylation may occur. (Structure 3) Hyperphosphorylated Gro/TLE interacts with histones and recruits HDAC1 to the template, leading to histone deacetylation. The ability of Gro/TLE to oligomerize may result in the engagement of adjacent nucleosomes by the Gro/TLE polymer, resulting in chromatin modification over an extended domain and transcriptional repression.