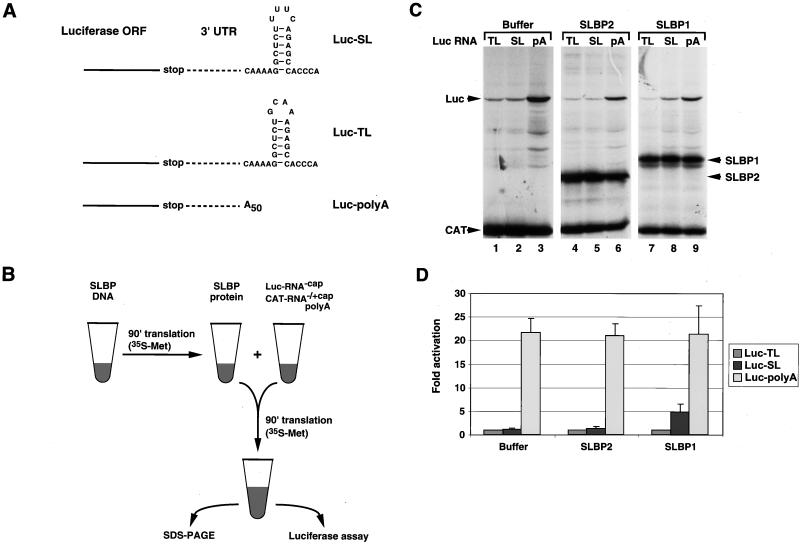
FIG. 1.
SLBP stimulates histone mRNA translation in vitro. (A) Structure of the 3′ end of the luciferase reporter mRNAs. The Luc-SL mRNA ends in the histone stem-loop that binds SLBP, the Luc-TL mRNA ends in a stem-loop that does not bind SLBP, and the Luc-polyA mRNA ends in a poly(A) tail 50 nt long. ORF, open reading frame. (B) Schematic of the in vitro translation assay. An aliquot of RRL was incubated either with buffer or with SLBP DNA in the presence of T7 RNA polymerase and [35S]methionine. After incubation for 90 min, an aliquot of the lysate was mixed with a fresh aliquot of reticulocyte lysate together with a luciferase uncapped reporter mRNA and a polyadenylated uncapped CAT mRNA as an internal standard. After incubation for 90 min at 30°C, the reaction products were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and the in vitro-synthesized proteins were detected by autoradiography. An aliquot of the assay was analyzed for luciferase activity by luminometry. (C) Lysates containing no SLBP (lanes 1 to 3), xSLBP2 (lanes 4 to 6), or xSLBP1 (lanes 7 to 9) were incubated with the standard polyadenylated CAT mRNA and the Luc-TL (lanes 1, 4, and 7), Luc-SL (lanes 2, 5, and 8), or Luc-polyA (lanes 3, 6, and 9) mRNA. The reaction products were analyzed by gel electrophoresis, and the proteins were detected by autoradiography. (D) The autoradiogram (panel C) was quantified, and relative luciferase activity was calculated. In addition, an aliquot of each reaction mixture was analyzed for luciferase activity with a luminometer. Quantification of the results by PhosphorImager and by luciferase assay yielded identical results. Panel D shows the results of an average of five experiments with five different batches of RRL, and the error bars represent the standard deviation. The fold activation is the result of luciferase activity from the Luc-SL and Luc-polyA mRNAs divided by the luciferase activity from the Luc-TL mRNA.