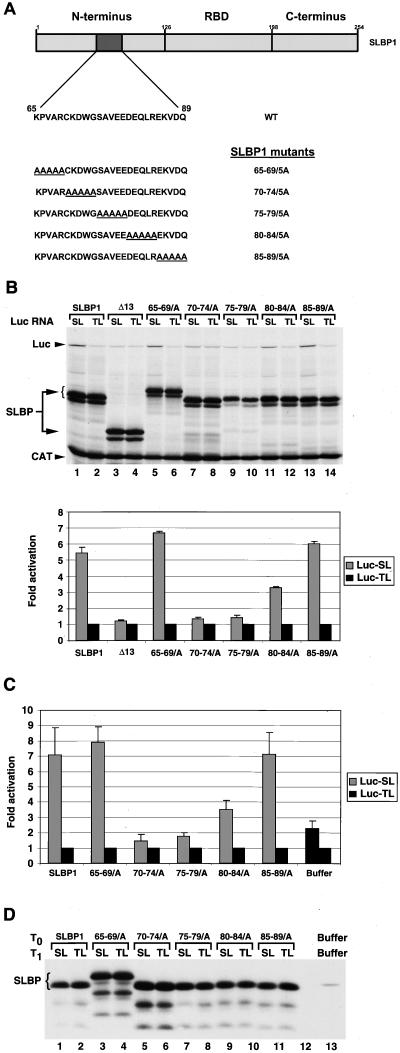
FIG. 8.
Alanine scanning of the xSLBP1 translation activation domain. (A) Amino acids 65 to 89 in the N-terminal region of xSLBP1 were replaced sequentially, five residues at a time, with five alanines (underlined). WT, wild type. (B) Lysates containing the five-alanine substitutions shown in panel A were incubated with the standard polyadenylated CAT mRNA and the Luc-TL or Luc-SL mRNA. Protein synthesis (top) and luciferase activity (bottom) were assayed as described in Fig. 1C and D, respectively. The bar graph shows the averages of two experiments with two different batches of RRL, and the error bars represent the standard deviations. (C) Oocytes injected at T0 with the xSLBP1 five-alanine substitution mRNAs and then again at T1 = 16 h with Luc-SL or Luc-TL mRNA in combination with R-Luc-SL mRNA were harvested at T2 = 32 h, processed, and analyzed for luciferase activity as described in Fig. 1C. The averages of two experiments with two different batches of oocytes are shown. The error bars represent the standard deviations. (D) A fraction corresponding to one oocyte worth of the same lysate used for the luciferase assay of panel C was used for detection of the xSLBP1 five-alanine substitution mutant proteins. The Western blot shown was performed as described previously. Oocytes injected at T0 and T1 with buffer show the level of endogenous xSLBP1 protein (lane 13).