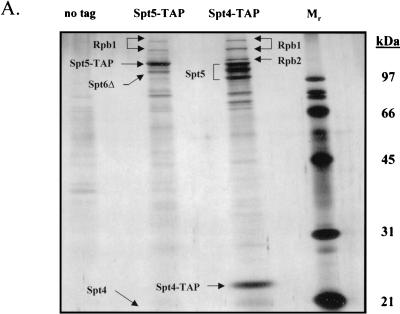
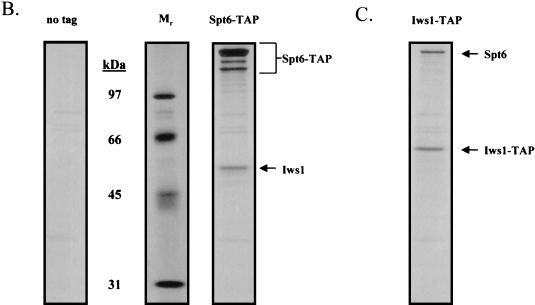
FIG. 1.
Isolation of protein complexes containing Spt4, Spt5, and Spt6. (A) TAPs of the Spt4/Spt5 complex were carried out on strains containing either no tagged protein or TAP-tagged versions of Spt4 or Spt5. Protein complexes were purified in the presence of 100 mM NaCl and were then analyzed by SDS-PAGE and silver staining. Spt4, Spt5, subunits of RNAPII, and a truncated form of Spt6 were identified by trypsin digestion and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. In the purification of tagged Spt5, the presence of Spt4 was identified by subjecting an aliquot of the eluate from the final column directly to trypsin digestion and tandem mass spectrometry. (B) TAP of Spt6. Purification using an extract containing a TAP-tagged version of Spt6 in 100 mM NaCl resulted in isolation of three forms of the tagged protein and a previously uncharacterized protein encoded by ORF YPR133c, whose gene product we have called Iws1 (interacts with Spt6). (C) TAP of Iws1. Tagging and isolation of Iws1 in 100 mM salt resulted in copurification of a stoichiometric amount of one form of Spt6. Because both Spt6-TAP and Iws1-TAP were run on the same gel, it could be concluded that Iws1 copurified with only the slowest-migrating form of Spt6.