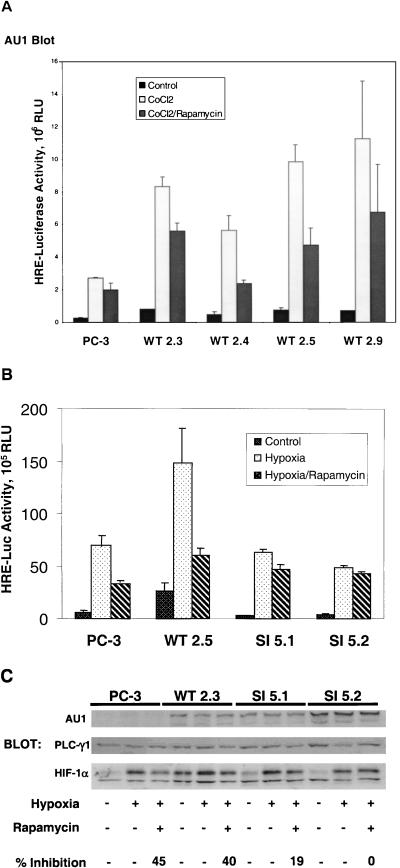
FIG. 5.
Activation of HIF-1 in stably transfected PC-3 sublines. PC-3 cells were stably transfected with an expression plasmid encoding either AU1-tagged, wild-type AmTOR (WT), or a rapamycin-resistant (Ser2035→Ile) AmTOR mutant (SI). Clonal sublines were cotransfected with the pHRE-luc reporter, together with a Renilla luciferase reporter (as a control for transfection efficiency). After 24 h, the culture medium was changed to RPMI 1640 supplemented with 0.1% FBS, and the cells were cultured for an additional 6 h. The cells were pretreated for 30 min with solvent vehicle or 100 nM rapamycin and then were stimulated for 16 h with 150 μM CoCl2 or hypoxia as indicated. Cell lysates were subjected to the dual luciferase assay, and sample values were normalized for variations in transfection efficiency based on the Renilla luciferase activity. Error bars represent the variance of duplicate samples. Aliquots of cell extracts were assayed for expression of the recombinant AmTOR protein by α-AU1 immunoblotting (upper panels). (A) AmTOR-WT-transfected subclones. (B) Comparison of AmTOR-WT- and AmTOR-SI-transfected subclones. (C) PC-3 cells and stably transfected WT or SI sublines wereprecultured for 8 h in medium containing 0.1% serum and then treated with either vehicle or rapamycin. After 30 min, the cells were stimulated for 16 h with hypoxia. Detergent-soluble proteins were immunoblotted sequentially with α-HIF-1α MAb and α-PLCγ1 antibodies. HIF-1α levels were determined by densitometric analysis, and the percent inhibition by rapamycin of hypoxia-induced HIF-1α expression was calculated for each sample set. In the upper panel, separate aliquots of the cell extracts were immunoblotted with α-AU1 MAb to detect the expression of the AmTOR-WT or AmTOR-SI proteins.