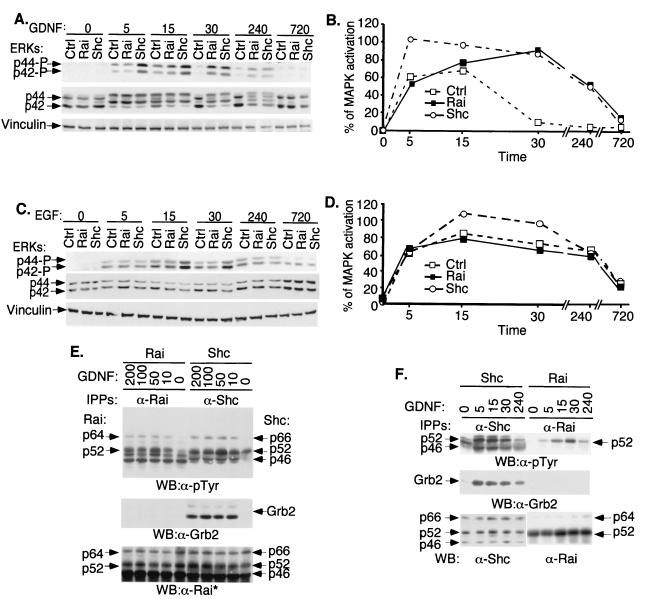
FIG. 3.
Tyrosine phosphorylation, Grb2 binding, and effects on MAPK activation of Rai proteins. (A) SK-N-BE(2) cells infected with the empty retroviral vector (Ctrl) or with vectors expressing Shc (Shc) or Rai (Rai) were serum deprived (24 h) and then stimulated for different time periods (0, 5, 15, 30, 240, or 720 min) with 100 ng of GDNF/ml. Lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against phosphorylated ERKs (upper panel), anti-ERK antibodies (middle panel), or vinculin (lower panel). (B) The quantitation of the MAPK activation results shown in panel A was determined as described in Materials and Methods. (C) The same cells described for panel A were serum deprived (24 h) and then stimulated for different time periods (0, 5, 15, 30, 240, or 720 min) with 100 ng of EGF/ml. Lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against phosphorylated ERKs (upper panel), anti-ERK antibodies (middle panel), or vinculin (lower panel). (D) The quantitation of the MAPK activation results shown in panel C was determined as described in Materials and Methods. (E) SK-N-BE(2) cells overexpressing Rai (Rai) or Shc (Shc) were serum starved (0) and then stimulated for 5 min with different doses of GDNF as indicated (in nanograms/milliliter) and lysed. Specific anti-Rai (anti-CH1 antibodies) (α-Rai) or anti-Shc (anti-CH1 antibodies) (α-Shc) immunoprecipitates (IPPs) were analyzed by Western blotting (WB) with anti-pTyr (α-pTyr) (upper panel), anti-Grb2 (α-Grb2) (middle panel), or anti-Rai (anti-SH2) (lower panel) antibodies. This anti-Rai antibody (anti-SH2) also recognizes overexpressed Shc polypeptides. (F) Specific anti-Rai (anti-CH1 antibodies) or anti-Shc (anti-CH1 antibodies) immunoprecipitates derived from the lysates of the experiment described for panel A were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-pTyr (upper panel), anti-Grb2 (middle panel), or anti-Rai (anti-CH1) and anti-Shc (anti-SH2) antibodies (lower panel).