Figure 3.
Sequence Conservation of the GNOM DCB Domain.
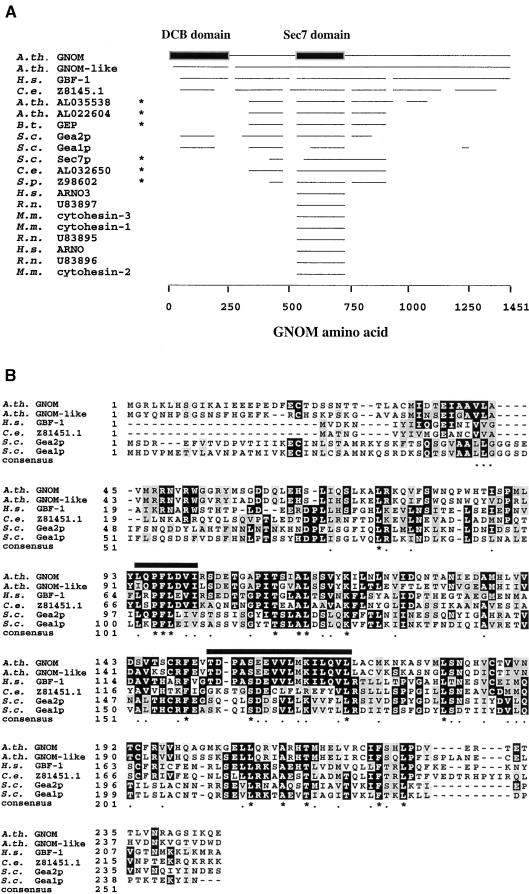
(A) GNOM homologs identified by BLAST P search (BLAST plus BEAUTY, ungapped alignments, expect value 0.0001; Altschul et al., 1997). Horizontal lines aligned with GNOM amino acid positions (bottom) represent regions of sequence conservation >38%. Asterisks indicate sequences with higher overall homology to Sec7p. GenBank accession numbers are indicated, and other references are as follows: A.th. GNOM, Arabidopsis GNOM/EMB30 (Shevell et al., 1994; Busch et al., 1996); A.th.GNOM-like, Arabidopsis GNOM-like putative protein (Sato et al., 1998); H.s. GBF-1, human GBF1 (Mansour et al., 1998); B.t. GEP, bovine Sec7-like GEP (Morinaga et al., 1997); S.c. Gea1p and Gea2p, budding yeast Gea1p and Gea2p (Peyroche et al., 1996); H.s. ARNO and ARNO 3, human ARNO (Chardin et al., 1996) and ARNO3 (Franco et al., 1998); M.m. cytohesin-1, -2, and –3, mouse cytohesin-1, -2, and -3 (Klarlund et al., 1997; Kim et al., 1998); cytohesin-1/B2-1 (Liu and Pohajdak, 1992); R.n. U83895, U83896, and U83897, rat sec7 domain proteins (Telemenakis et al., 1997); C.e. Z8145.1 and AL032650, C. elegans protein; and S.p. Z98602, fission yeast protein.
(B) Clustal W (Thompson et al., 1994) alignment of GNOM DCB domain homology regions. Sequence identities (conservation) to the DCB domain are 70% (81%) for Arabidopsis GNOM-like putative protein amino acids 20 to 225, 38% (58%) for human GBF1 amino acids 34 to 227, 30% (53%) for Gea2p amino acids 88 to 230, 24% (53%) for Gea1p amino acids 87 to 226, and 26% (48%) for C.e. Z81451.1 amino acids 88 to 226 (Z81451.1 has a 33–amino acid insertion at position 138, which is not shown for simplicity of alignment). Black boxes indicate identity, and grey boxes indicate homology between at least three sequences. Consensus derived from identical and conserved amino acids of all six sequences is indicated as stars and dots. Black bars overline a conserved proline-phenylalanine-leucine (PFL) motif and a hydrophobic helix.