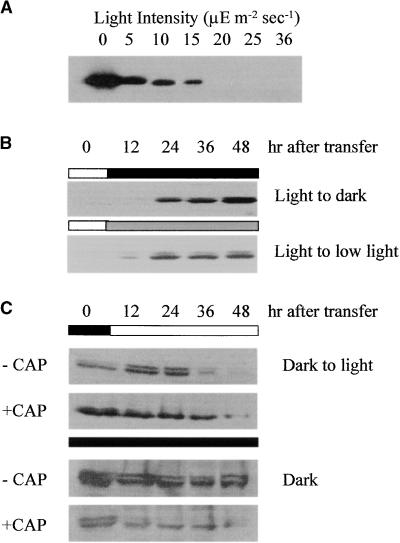
Figure 4.
Protein Gel Blot Analysis of CHLL Accumulation and Turnover in Wild-Type Cells under Various Growth Conditions.
(A) The effect of light intensity on CHLL content in wild-type cells was examined by protein gel blot analysis. Total cellular extracts were prepared from the same number of cells grown in the dark or for 48 hr under the light intensity indicated. The extracts were fractionated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and reacted with antiserum detecting CHLL.
(B) Accumulation of CHLL in wild-type cells at various times after transfer of the cultures from growth in the light (75 to 100 μmol m−2 sec−1) to darkness or low-light (5 μmol m−2 sec−1) growth conditions.
(C) Effects of chloramphenicol on CHLL formation and accumulation in wild-type cells. Dark-grown wild-type cells were treated with chloramphenicol (+CAP) (100 μg/mL), and the quantities of CHLL formed were determined by protein gel blot analysis at various times after continued growth in darkness or after transfer to high-intensity light (75 to 100 μmol m−2 sec−1) growth conditions. Control cells not treated with chloramphenicol (−CAP) were grown under the same conditions and sampled at the same times.