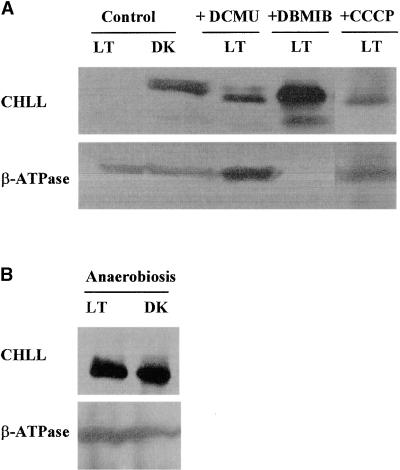
Figure 5.
Effects of Various Cell Metabolic Inhibitors and Photosynthetic Electron Transport Uncouplers on CHLL Quantities in Wild-Type Chlamydomonas Cells.
Shown are the effects of various metabolic inhibitors and photosynthetic electron transport uncouplers on the synthesis or accumulation of CHLL. Wild-type Chlamydomonas cells were grown in Tris-acetate-phosphate medium in the light (LT; >50 μmol m−2 sec−1) or darkness (DK) in the presence (+) or absence (Control) of various pharmacological treatments. Whole-cell extracts were prepared, and CHLL quantities were measured by immunoblot analysis. As an internal control, the amounts of the β subunit of the chloroplast coupling factor CF1-ATPase (β-ATPase) were measured.
(A) CHLL content in untreated (Control) light- and dark-grown wild-type cells and light-grown wild-type cells 48 hr after treatment with 1 μM CCCP, 10 μM DCMU, or 10 μM DBMIB (+CCCP, +DCMU, and +DBMIB, respectively).
(B) CHLL content in light- and dark-grown wild-type cells 48 hr after induction of anaerobic growth conditions by purging cultures with argon.