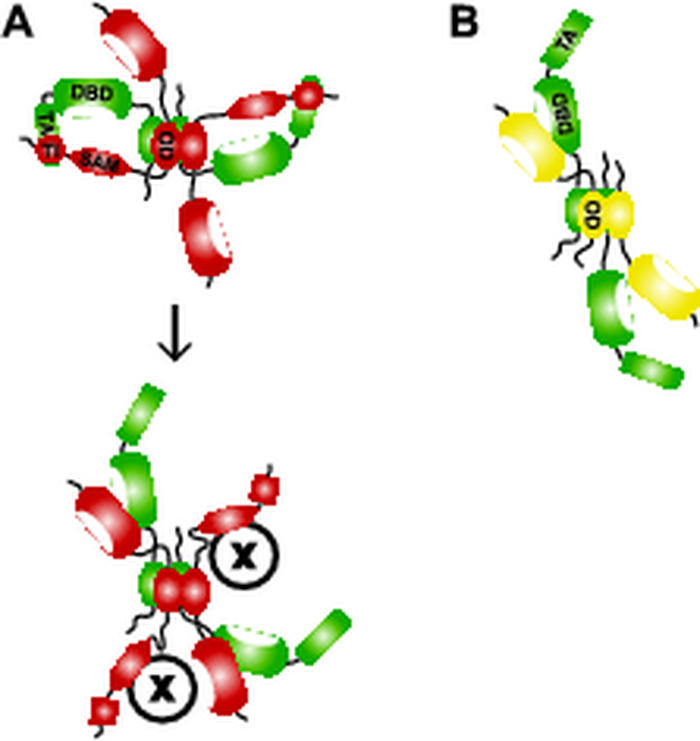
FIG. 8.
Models of p63 heterotetramers. (A) In a tetramer consisting of two TAp63γ (green) and two ΔNp63α (red) monomers, the TI domains of ΔNp63α can interact with and inhibit both TA domains of the TAp63γ monomers. Activation of this tetramer could occur by recruiting another protein, e.g., a kinase that disrupts the TI-TA domain interaction. Binding of kinase or the other factor, illustrated as “X,” could be facilitated by the SAM domain. (B) Tetramerization of two TAp63γ monomers (green) with two ΔNp63γ monomers (yellow) leaves both TA domains active.