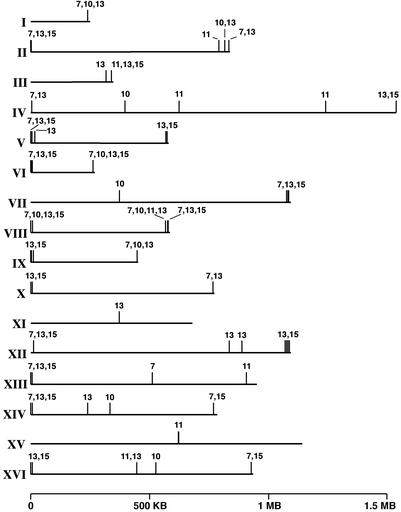
Figure 3.
Mutations in the histone H4 tail result in a general down-regulation of telomere proximal genes. Transcriptional changes between strains with mutant and wild-type histone H4 were determined by competitive hybridization to DNA microarrays. Each array contained >6,000 S. cerevisiae ORFs, and each hybridization was carried out a minimum of two times. A schematic of each S. cerevisiae chromosome is presented. Vertical lines above each chromosome mark loci that were transcriptionally down-regulated in the mutant strain. Numbers above these lines correspond with residue position number (e.g., G11T) in the mutants that showed an effect. For alleles L10F and G11T, the 10 loci that were down-regulated the most are indicated, for G7I and A15T ≈20 loci and for G13L ≈30 loci are shown.