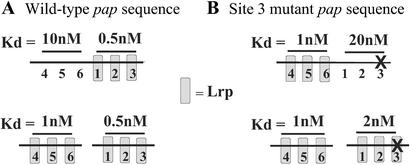
Figure 5.
Quantitation of the mutual exclusion effect on LRP binding by UV footprint analysis. DNA fragments containing the intact pap regulatory region (Upper) or unlinked regions containing only Lrp binding sites 1–3 or 4–6 (110 bp each) (Lower) were cloned into plasmid vector pTZ19U (41). Supercoiled plasmids were isolated from a Dam− strain, and the affinity of Lrp for sites 1–3 and 4–6 was measured by UV footprinting as described (42). Briefly, samples were irradiated at 254 nm, and UV-induced pyrimidine dimers were detected by extension of 32P-end-labeled primers with TaqDNA polymerase. The affinities of Lrp for pap DNA sites 1–3 and 4–6 were identical to affinities determined by using electrophoretic mobility shift analysis (unpublished data). The location of a 6-bp substitution mutation in site 3 (see Fig. 1) is depicted by an “X” in B.