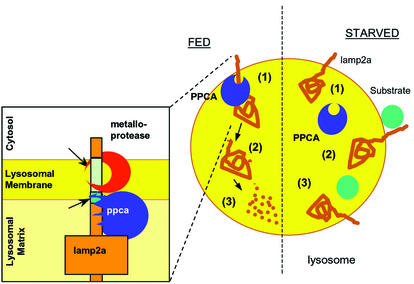
Fig. 8. Hypothetical model for the regulation of CMA by PPCA. Under normal nutritional conditions (FED, left), binding of PPCA to the lysosomal membrane might trigger cleavage of lamp2a by an unidentified metalloprotease (at the transmembrane region) (1) and by PPCA (at the intersection between the transmembrane and luminal regions) (see inset). That cleavage releases a truncated lamp2a into the matrix (2), where it is completely degraded by the lysosomal proteases (3). During starvation (right), PPCA dissociates from the lysosomal membrane (1) so that lamp2a is not longer degraded and remains in the membrane, accessible for substrate binding (2) and uptake into the lysosomes (3).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.