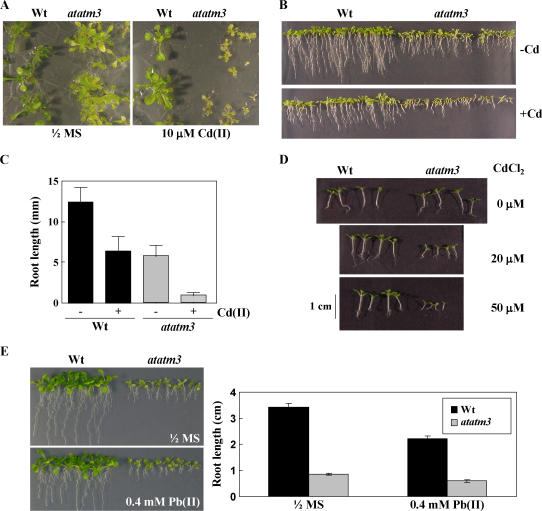
Figure 5.
Phenotypes of wild-type and atatm3 mutant plants grown on Cd(II)-containing plates. A, Effect of Cd(II) on the shoot growth of the AtATM3 knockout mutant (atatm3). Seeds were germinated on horizontally placed 0.5× MS Suc plates (0.6% agar) containing 10 μm CdCl2 and grown for 20 d under 16-h light. B, Effects of Cd(II) on root growth of atatm3 and wild-type plants. Seeds were germinated and grown vertically on KH2PO4 (200 mg/L), MgSO4·7H2O (187.5 mg/L), Ca(NO3)·4H2O (79.25 mg/L), KNO3 (22 mg/L), Fe-EDTA (17.5 mg/L), MnCl2·4H2O (48.75 μg/L), H3BO3 (76.25 μg/L), ZnSO4·7H2O (12.25 μg/L), CuSO4·5H2O (6.875 μg/L), NaNoO4·2H2O (12.5 μg/L), and Ni(NO3)2·6H2O (3.75 μg/L) agar plates in the absence or presence of 15 μm CdCl2 for 8 d with 16-h light. C, Root length of atatm3 and wild-type seedlings shown in B. Bar = sd. D, Effects of Cd(II) on growth of atatm3 and wild-type plants under 8-h-light/16-h-dark conditions. Seeds were germinated and grown horizontally on 0.5× MS Suc agar plates in the presence of increasing Cd(II) concentrations (0, 20, and 50 μm CdCl2) for 13 d. E, Effect of Pb(II) on the growth of the atatm3 mutant. Seeds were germinated and grown vertically on 0.5× MS medium with or without 0.4 mm Pb(NO3)2 for 2 weeks under a 16-h light cycle.