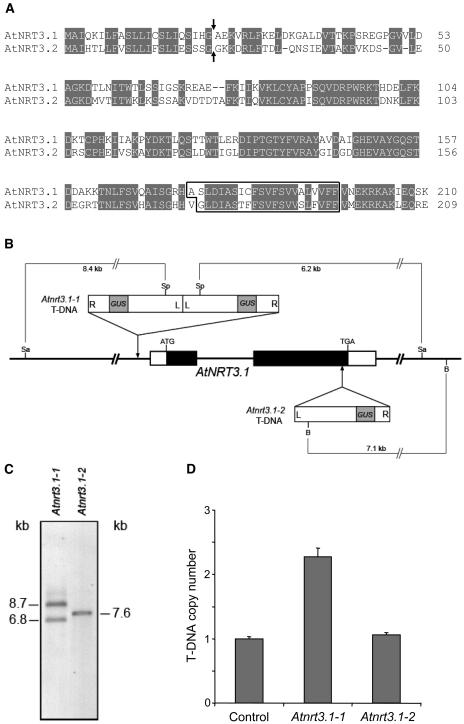
Figure 1.
Amino acid sequences of AtNRT3 proteins and characterization of Atnrt3.1 T-DNA lines. A, Amino acid sequence comparison of AtNRT3.1 and AtNRT3.2. Identical amino acids are shaded. Arrows indicate predicted cleavage sites. The transmembrane region predicted by TMHMM (Krogh et al., 2001) is boxed. B, Schematic diagram of AtNRT3.1 with the T-DNA insertions. In AtNRT3.1 white boxes indicate 5′ or 3′ untranslated region, and black boxes indicate open reading frame. The T-DNAs in the Atnrt3.1-1 and Atnrt3.1-2 mutants are inserted 186 bp upstream of the first putative start codon, and 63 bp before the stop codon, respectively. The diagram is not drawn in scale. R, Right border; L, left border; Sa, SalI; Sp, SphI; B, BamHI. C, The Southern blot of the Atnrt3.1 mutants. Genomic DNAs of Atnrt3.1-1 and Atnrt3.1-2 were digested with SalI/SphI and BamHI, respectively, and probed with a 1.2-kb fragment of GUS gene (Kaiser et al., 2002). D, The T-DNA copy number in the Atnrt3 mutants measured by relative quantitative real-time PCR. Each sample was normalized by nitrite reductase (a single copy gene, AGI code: At2g15620), and expressed relative to the control T-DNA line (M. Galli, unpublished data).