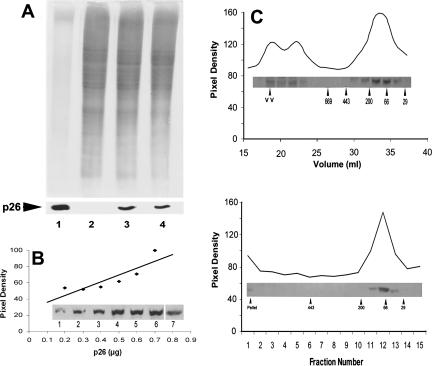
Fig 2.
p26 from E11′L cells. (A) Protein extracts from E11′L cells were electrophoresed in 12.5% SDS polyacrylamide gels and either stained with Coomassie blue (upper panel) or blotted to nitrocellulose and immunostained with antibody to p26 (lower panel). Lane 1: 10.0 and 5.0 μg of Artemia embryo protein for gel and blot, respectively; lane 2: 30 μg of protein extract from 293H cells transfected with vector only; lane 3: 30 μg of protein extract from E11′L cells early in culture; lane 4: 30 μg of protein extract from E11′L cells after 50 days in culture. (B) E11′L protein extract and purified p26 produced in bacteria were electrophoresed concurrently in 12.5% gels, blotted to nitrocellulose, probed with anti-p26 antibody, and scanned with the UMAX Astra 1200S scanner. The amount of p26 was determined by comparing the p26 band pixel density in the E11′L lane to the standard curve derived with bacterially produced p26. Insert lane 1: 0.2 μg; lane 2: 0.3 μg; lane 3: 0.4 μg; lane 4: 0.5 μg; lane 5: 0.6 μg; lane 6: 0.7 μg of protein. Lane 7 contained 40 μg of E11′L cell protein. (C) Protein extracts from E11′L cells were either chromatographed in Sepharose 6B columns (upper panel) or centrifuged in 10–50% continuous sucrose gradients (lower panel). Collected fractions were electrophoresed in 12.5% SDS polyacrylamide gels, blotted to nitrocellulose, and immunostained with antibody to p26 (inserts). Labeled arrowheads, molecular mass markers × 10−3