Abstract
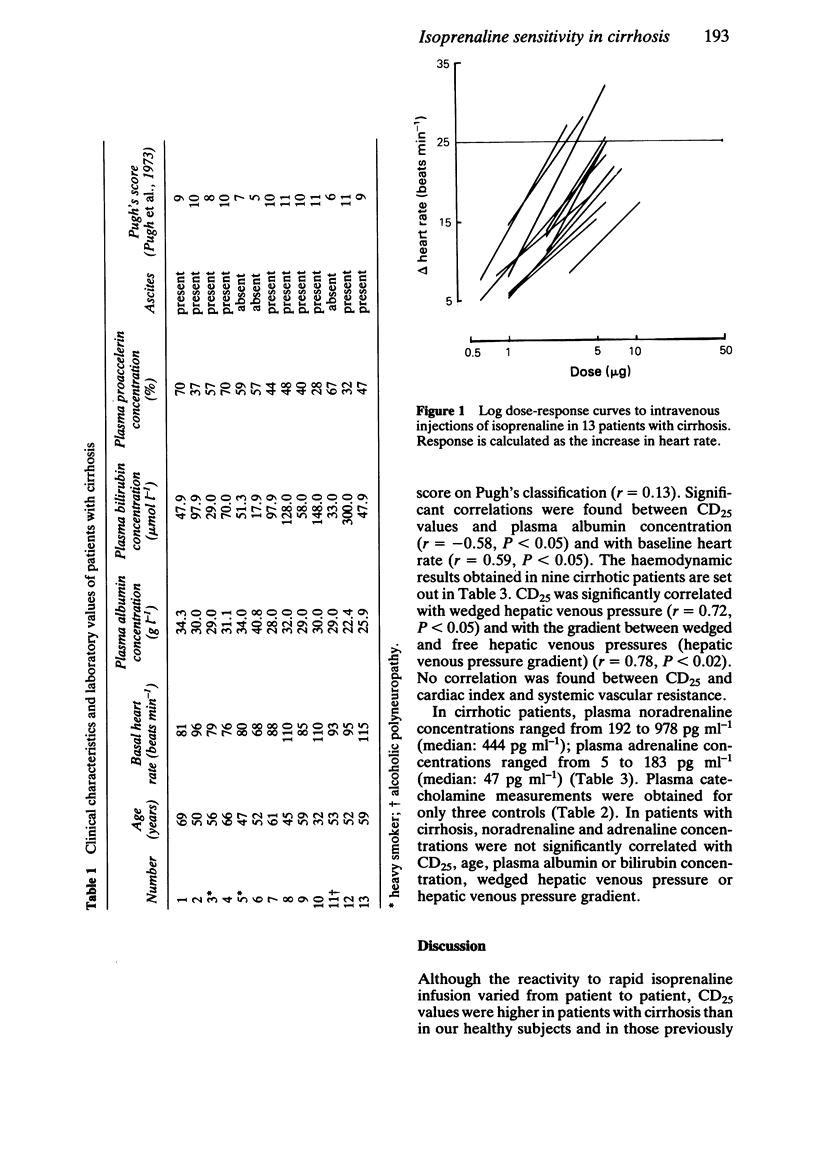
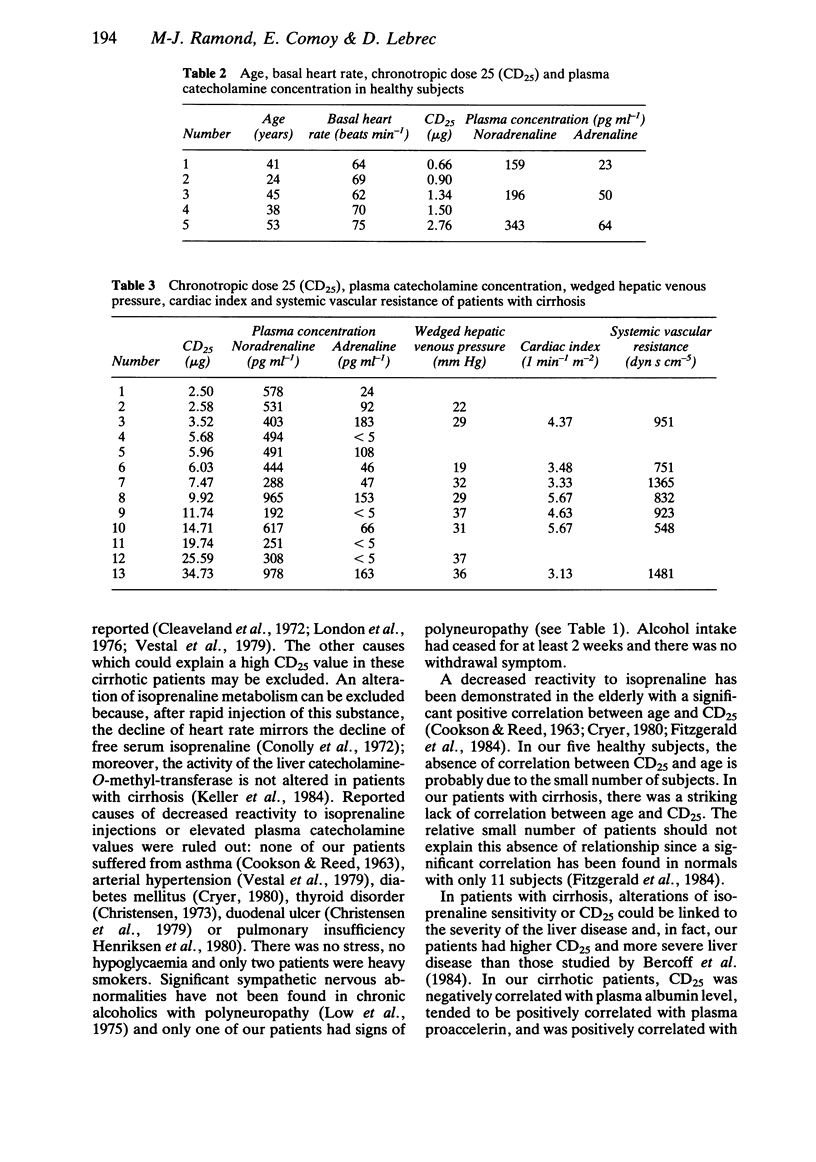
Isoprenaline sensitivity and plasma catecholamine concentrations were studied to assess the sympathetic nervous activity in 13 patients with alcoholic cirrhosis and were compared with five controls. In patients with cirrhosis, the dose of isoprenaline required to increase the resting heart rate by 25 beats min-1 (chronotropic dose 25 or CD25) ranged from 2.50 to 34.73 micrograms (median: 4.47 micrograms) and was significantly higher than in controls (range: 0.66 to 2.76 micrograms, median: 1.34 micrograms). In cirrhotic patients, CD25 values were significantly correlated with plasma albumin concentration, resting heart rate and wedged hepatic venous pressure. In patients with cirrhosis, plasma noradrenaline concentrations ranged from 192 to 978 pg ml-1 (median: 444 pg ml-1) and adrenaline concentrations ranged from 5 to 183 pg ml-1 (median: 47 pg ml-1). No correlation was found between noradrenaline or adrenaline concentrations and CD25 values in cirrhotic patients. In conclusion, in patients with cirrhosis, beta-adrenoceptor responsiveness assessed by isoprenaline sensitivity is altered.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bercoff E., Bataille C., Pariente A. E., Valla D., Delhotal B., Lebrec D. Assessment of beta-adrenergic blockade with propranolol in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):451–453. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi M., Trevisani F., Santini C., Ligabue A., Capelli M., Gasbarrini G. Impairment of blood pressure control in patients with liver cirrhosis during tilting: study on adrenergic and renin-angiotensin systems. Digestion. 1982;25(2):124–130. doi: 10.1159/000198820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchet L., Lebrec D. Changes in splanchnic blood flow in portal hypertensive rats. Eur J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;12(4):327–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1982.tb02240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKSON D. U., REED C. E. A COMPARISON OF THE EFFECTS OF ISOPROTERENOL IN THE NORMAL AND ASTHMATIC SUBJECT. A PRELIMINARY REPORT. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1963 Nov;88:636–643. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1963.88.5.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J., Brandsborg O., Løvgreen N. A., Brandsborg M. Elevated plasma noradrenaline concentrations in duodenal ulcer patients are not normalized by vagotomy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Sep;49(3):331–334. doi: 10.1210/jcem-49-3-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J. Plasma noradrenaline and adrenaline in patients with thyrotoxicosis and myxoedema. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Aug;45(2):163–171. doi: 10.1042/cs0450163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaveland C. R., Rangno R. E., Shand D. G. A standardized isoproterenol sensitivity test. The effects of sinus arrhythmia, atropine, and propranolol. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Jul;130(1):47–52. doi: 10.1001/archinte.130.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conolly M. E., Davies D. S., Dollery C. T., Morgan C. D., Paterson J. W., Sandler M. Metabolism of isoprenaline in dog and man. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Nov;46(3):458–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E. Physiology and pathophysiology of the human sympathoadrenal neuroendocrine system. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 21;303(8):436–444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008213030806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Prada M., Zürcher Simultaneous radioenzymatic determination of plasma and tissue adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine within the femtomole range. Life Sci. 1976 Oct 15;19(8):1161–1174. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Even P., Nicollo F., Benhamou J. P., Fauvert R. Le débit cardiaque au cours des maladies du foie. Effets de l'anastomose porto-cave et des diurétiques. Rev Int Hepatol. 1966;16(4):955–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald D., Doyle V., Kelly J. G., O'Malley K. Cardiac sensitivity to isoprenaline, lymphocyte beta-adrenoceptors and age. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Jun;66(6):697–699. doi: 10.1042/cs0660697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. F., Conolly M. E., Fenyvesi T., Briant R., Dollery C. T. Intravenously administered isoproterenol sulfate dose-response curves in man. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Sep;130(3):361–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen J. H., Christensen N. J., Kok-Jensen A., Christiansen I. Increased plasma noradrenaline concentration in patients with chronic obstructive lung disease: relation to haemodynamics and blood gases. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1980 Sep;40(5):419–427. doi: 10.3109/00365518009101864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen J. H., Ring-Larsen H., Christensen N. J. Sympathetic nervous activity in cirrhosis. A survey of plasma catecholamine studies. J Hepatol. 1985;1(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOWALSKI H. J., ABELMANN W. H. The cardiac output at rest in Laennec's cirrhosis. J Clin Invest. 1953 Oct;32(10):1025–1033. doi: 10.1172/JCI102813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller U., Gerber P. P., Bühler F. R., Stauffacher W. Role of the splanchnic bed in extracting circulating adrenaline and noradrenaline in normal subjects and in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 Jul;67(1):45–49. doi: 10.1042/cs0670045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Bataille C., Bercoff E., Valla D. Hemodynamic changes in patients with portal venous obstruction. Hepatology. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):550–553. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Goldfarb G., Degott C., Rueff B., Benhamou J. P. Transvenous liver biopsy: an experience based on 1000 hepatic tissue samplings with this procedure. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):338–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Hillon P., Muńoz C., Goldfarb G., Nouel O., Benhamou J. P. The effect of propranolol on portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis: a hemodynamic study. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):523–527. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Stiles G. L. Mechanisms of membrane-receptor regulation. Biochemical, physiological, and clinical insights derived from studies of the adrenergic receptors. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 14;310(24):1570–1579. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406143102406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London G. M., Safar M. E., Weiss Y. A., Milliez P. L. Isoproterenol sensitivity and total body clearance of propranolol in hypertensive patients. J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;16(4):174–183. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1976.tb01514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A., Walsh J. C., Huang C. Y., McLeod J. G. The sympathetic nervous system in alcoholic neuropathy. A clinical and pathological study. Brain. 1975 Sep;98(3):357–364. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunzer M. R., Newman S. P., Bernard A. G., Manghani K. K., Sherlock S. P., Ginsburg J. Impaired cardiovascular responsiveness in liver disease. Lancet. 1975 Aug 30;2(7931):382–385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92896-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh R. N., Murray-Lyon I. M., Dawson J. L., Pietroni M. C., Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Aug;60(8):646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring-Larsen H., Hesse B., Henriksen J. H., Christensen N. J. Sympathetic nervous activity and renal and systemic hemodynamics in cirrhosis: plasma norepinephrine concentration, hepatic extraction, and renal release. Hepatology. 1982 May-Jun;2(3):304–310. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valla D., Bercoff E., Menu Y., Bataille C., Lebrec D. Discrepancy between wedged hepatic venous pressure and portal venous pressure after acute propranolol administration in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jun;86(6):1400–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valla D., Poynard T., Bercoff E., Bataille C., Goldfarb G., Lebrec D. Le syndrome d'hypercinésie circulatoire systémique chez les malades atteints de cirrhose. Relations avec l'insuffisance hépatocellulaire et l'hypertension portale. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1984 Apr;8(4):321–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestal R. E., Wood A. J., Shand D. G. Reduced beta-adrenoceptor sensitivity in the elderly. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Aug;26(2):181–186. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979262181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorobioff J., Bredfeldt J. E., Groszmann R. J. Hyperdynamic circulation in portal-hypertensive rat model: a primary factor for maintenance of chronic portal hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):G52–G57. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.1.G52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


