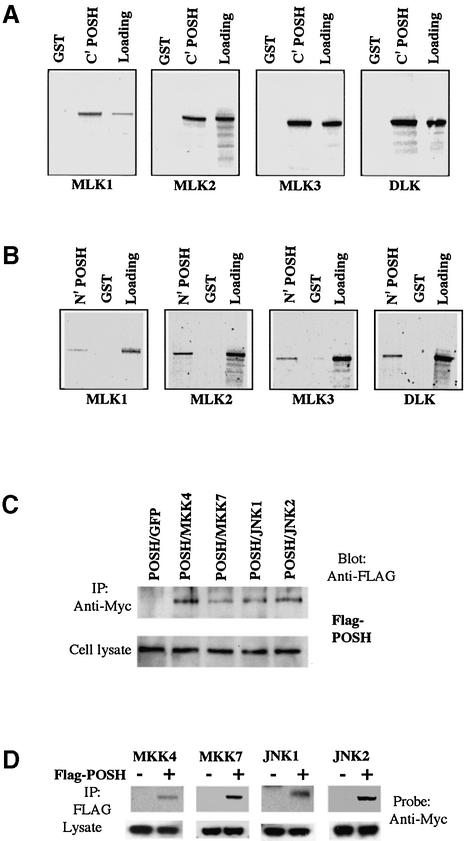
Fig. 4. POSH interacts with MLK family members in vitro and with MKK4/7 and JNK1/2 in vivo. (A and B) The POSH C- and N-termini interact with the MLKs in vitro. (A) The C-terminal half of POSH was fused in-frame with GST to form GST–POSH C′ fusion protein, which was expressed and purified as described in Materials and methods. GST–POSH C′ fusion protein was incubated with in vitro translated 35S-labeled full-length MLK family members (MLK1, MLK2, MLK3 and DLK) for the pull-down assays as described in Materials and methods. After extensive washing, radioactive protein that was retained was visualized by SDS–PAGE followed by autoradiography. (B) As in (A), except that the assay used the N-terminal half of POSH. (C and D) POSH co-immunoprecipitates with MKK4/7 and JNK1/2. 293 cells were transfected with expression vectors (pCMS.EGFP) encoding Flag epitope-tagged POSH and Myc epitope-tagged MKK4 and 7, JNK1 and 2, either alone or in combination as indicated. At 20 h post-transfection, cell extract was prepared and analyzed as in (A) for the transfection efficiency of different constructs. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody (C), and the immunocomplexes were analyzed for the presence of POSH with anti-Flag antibody. In reciprocal co-expression/immunoprecipitation experiments (D), cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody and the immunocomplexes were probed for the presence of MKK4, MKK7, JNK1 and JNK2 with anti-Myc antibody.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.