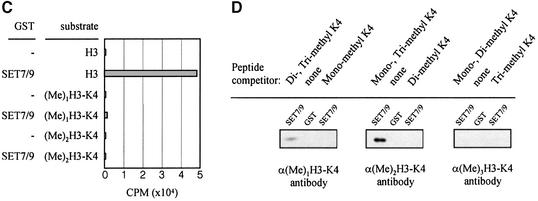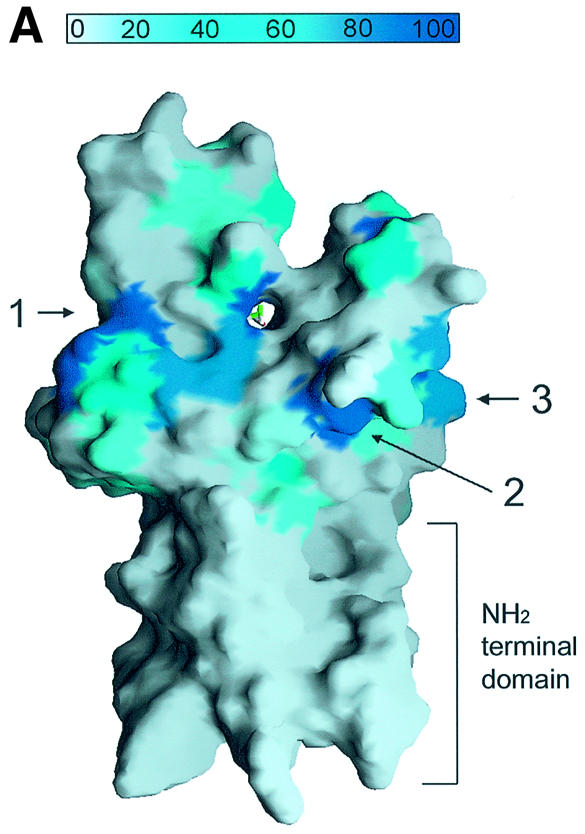
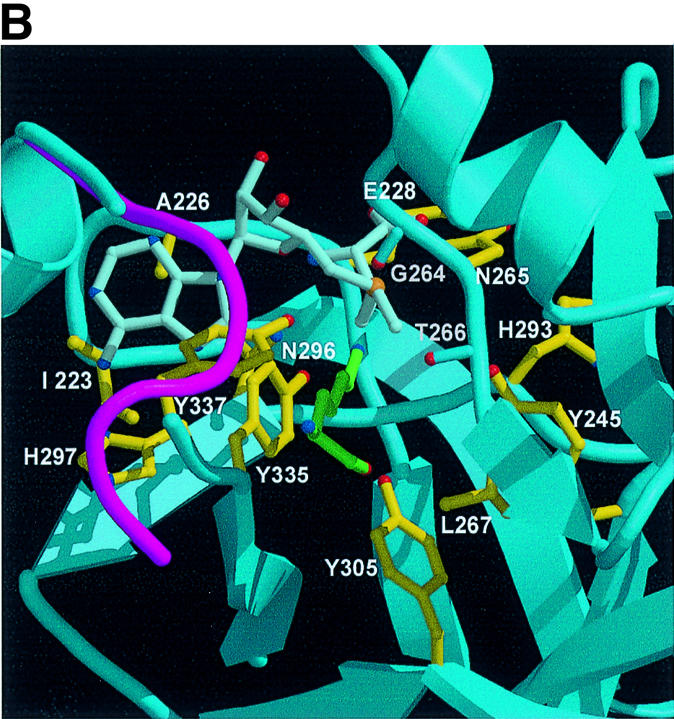
Fig. 4. A channel at the active site pocket. (A) A surface representation showing the location of the putative lysine-binding channel and a conserved shallow groove for the substrate-binding site (indicated by an arrow). See the text for sites 1, 2 and 3. The colouring scheme is identical to that in Figure 3A. AdoMet is shown in a bond model. The N-terminal domain is not coloured since it is not homologous to those of other SET-containing HMTases (Figure 1B). (B) A diagram showing the substrate-specific channel in SET7/9S. Key residues discussed in the text are shown in a ball-and-stick model. The AdoMet molecule is shown with the same colour scheme as in Figure 3B. (C) SET7/9 methylates unmethylated H3 peptide but cannot add methyl group(s) to already methylated peptide. An N-terminal peptide with amino acids 1–8 of unmodified, mono- or dimethylated H3-K4 was used for the assay of SET7/9 HMTase activity. The full-length SET7/9 was used for the assay. (D) Methylation specificity of SET7/9. Histone H3 (Roche) was methylated by SET7/9. The reaction products were resolved by SDS–PAGE, blotted to nitrocellulose and probed with either a H3-K4 mono- or dimethyl antibody, or a H3-K4 trimethyl antibody as indicated. The H3-K4, K9 trimethyl antibody also gave the same result as that of the H3-K4 trimethyl antibody (data not shown).