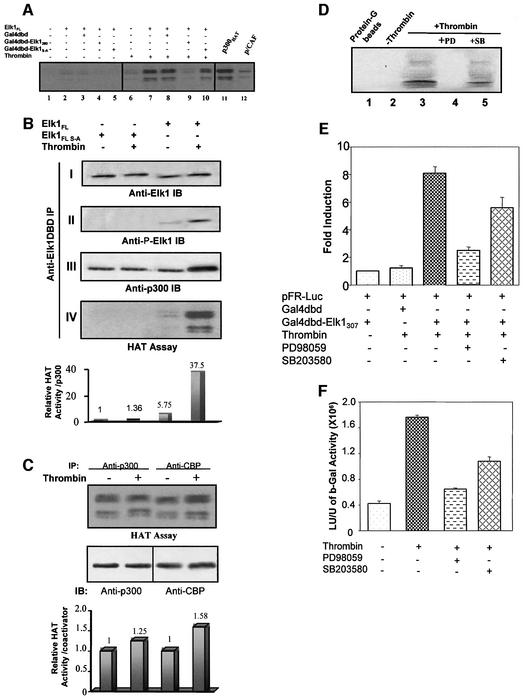
Fig. 5. HAT activity in the Elk-1–p300 complex after thrombin stimulation. (A) Elk-1FL–p300 complex-associated HAT activity was examined on protein G–Sepharose beads. Purified recombinant p300 HAT domain (lane 11) and full-length GST–p/CAF (lane 12) served as positive controls, and glutathione–agarose/protein G–Sepharose beads only as negative control. Elk-1-associated HAT activity was observed in cells stimulated by thrombin when Elk-1FL was present, except when competed out by Gal4-Elk-1260. (B) Elk-1 conformation is critical for associated p300 activity. Elk-1FL S-A (0.2 µg of plasmid) was co-transfected with p300 (2 µg of plasmid). Experiments similar to those in Figure 4 and in (A) were performed to test Elk-1-associated p300 HAT activity. Panel I: a similar level of Elk-1 proteins. Panel II: thrombin stimulated Ser383 phosphorylation of Elk-1FL protein but not of the mutant. Panel III: Elk-1–p300 interaction. Thrombin induces a 2.4-fold affinity increase upon Elk-1FL phosphorylation. Panel IV: HAT activity of the Elk-1-associated complex. Densitometry analysis of HAT activity (graph below panel IV) records the sum of densities of bands (representing H1–H4 acetylation) in each lane. The density of HAT activity bands was divided by the density of p300 bands detected by western blot in the corresponding lanes in panel III, and the results are shown in lane 1, to which we assigned a value of 1. Comparison of lanes 3 and 4 shows a 7-fold increase in HAT activity upon thrombin-stimulated phosphorylation of Elk-1FL. HAT activity from the S-A mutant was undetectable. (C) Nuclear extracts from cells transfected with 3 µg of p300 or CBP expression vectors were collected with or without 15 min thrombin treatment. α-p300 or α-CBP immunoprecipitation was performed to separate and concentrate the corresponding protein. Both co-activators show a slight increase in HAT activity, but the magnitude is small compared with changes observed when p300 is associated with Elk-1. (D) Thrombin-stimulated Elk-1-associated HAT activity can be eliminated by 25 µM of the MEK1/ERK2 inhibitor PD98509 (lane 4) and partially inhibited by 20 nM of the p38 inhibitor SB203580 (lane 5). The Gal4dbd–Elk-1307 fusion protein system (E) and the cIL-8-p683-luciferase reporter (F) were used to detect the relationship between inhibition of HAT activity and inhibition of transcriptional activity; inhibitor results are similar to those in (D).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.