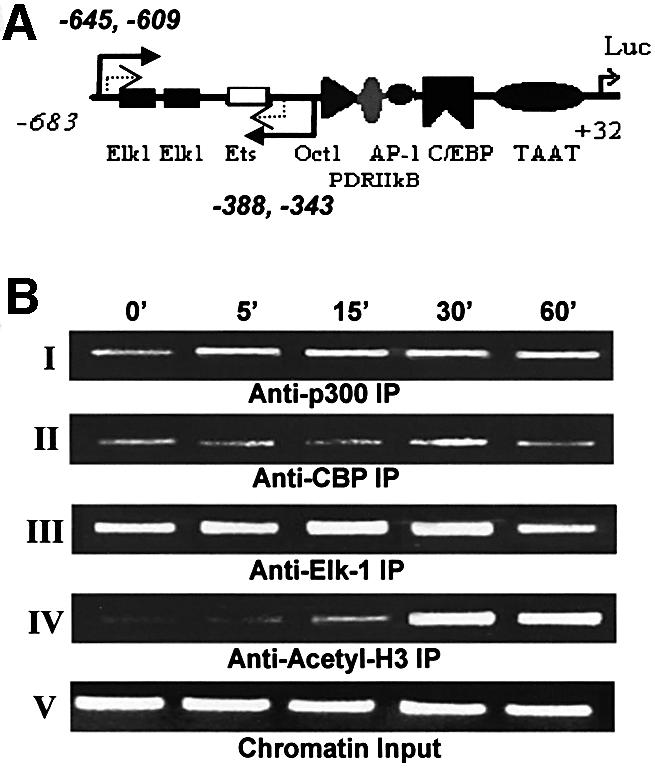
Fig. 6. Dynamics of the cIL-8 promoter-associated Elk-1 complex analyzed by ChIP. Fibroblasts were treated with thrombin over time (0–60 min), and chromatin DNA with associated proteins was cross-linked with formaldehyde. Various antibodies were used to precipitate different proteins, then DNA was released from the complex and purified to serve as a template for PCR. The cIL-8 promoter region containing Elk-1 elements was amplified specifically by two rounds of nested PCR. The amount of DNA represents the degree of occupancy of cIL-8 Elk-1 sites in the cell population. The primer choice is marked by the solid and dashed arrows in (A). The first round of PCR amplified the sequence corresponding to –645 to –343 of the cIL-8 promoter, which contains two Elk-1 elements and an Ets element, which potentially binds to Elk-1 with lower affinity. The second round of PCR was performed with the addition of nested primers specific for the –609 to –388 region to amplify the signal and avoid false priming. (B) ChIP resulted in a 222 bp band after two rounds of PCR. Panels I and II: immunoprecipitation with α-p300 and α-CBP shows the assembly of transcription activator and co-activator complex during treatment with thrombin. Panel III: immunoprecipitation with α-Elk-1 illustrates Elk-1 elements–transcription factor binding. Panel IV: immunoprecipitation with α-acetyl-H3 shows histone acetylation in the proximal promoter region of Elk-1. Panel V shows equal loading of chromatin components before precipitation.
