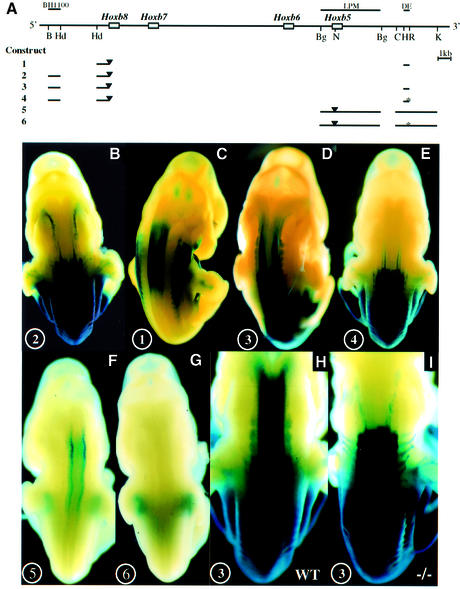
Fig. 4. The DE RARE mediates an RA-dependent rostral shift of 5′ Hoxb gene expression into the hindbrain. (A) Reporter constructs. The physical map of the Hoxb cluster with the Hoxb5–Hoxb8 genes is shown at the top. Regulatory sequences relevant for this study are shown as lines above the cluster. Below: lines depict the regions that are included in the reporter constructs. Black triangles represent the insertion site of the lacZ gene. The mutations in the two half-sites of the RARE are indicated by an asterisk. DE, distal element; LPM, lateral plate mesoderm; B, BamHI; Hd, HindIII; Bg, BglII; N, NcoI; C, ClaI; H, HincII; R, EcoRI; K, KpnI. (B–E) In vivo properties of the DE combined with the Hoxb8 promoter and proximal regulatory elements. Construct numbers are indicated on the lower left of the panels. (B) E11.5 embryos expressing construct 2 (Hoxb8BH1100); (C) construct 1 (Hoxb8DE); (D) construct 3 (Hoxb8BH1100 + DE); and (E) construct 4 (Hoxb8BH1100 + DE with mutated RARE). (F and G) In vivo properties of the DE combined with the Hoxb5 promoter and a proximal mesoderm-specific element (Sharpe et al., 1998). (F) E11.5 embryos expressing construct 5 (Hoxb5LPM + DE); and (G) E11.5 embryos expressing construct 6 (Hoxb5LPM + DE with mutated RARE). (H and I) RA dependence of the DE activity. E11.5 embryo expressing construct 3 in the presence (I) or absence (H) of the Raldh2-null mutation.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.