Abstract
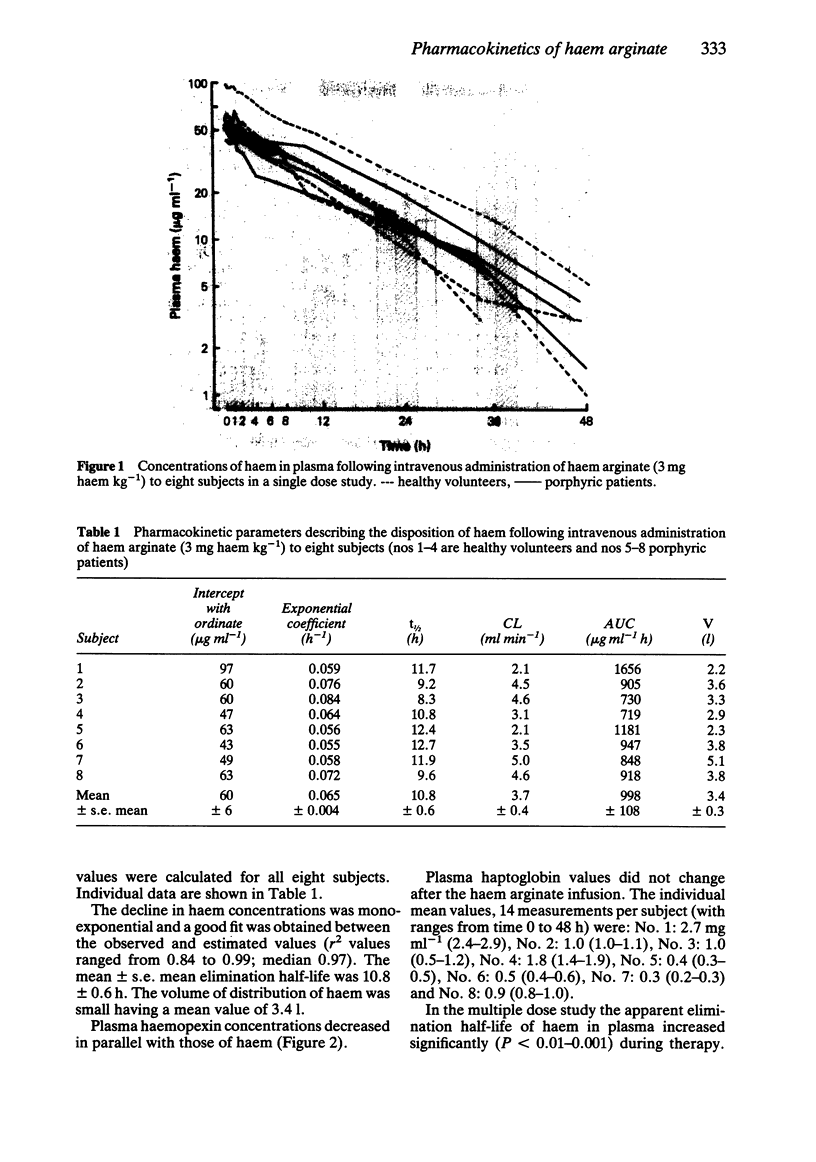
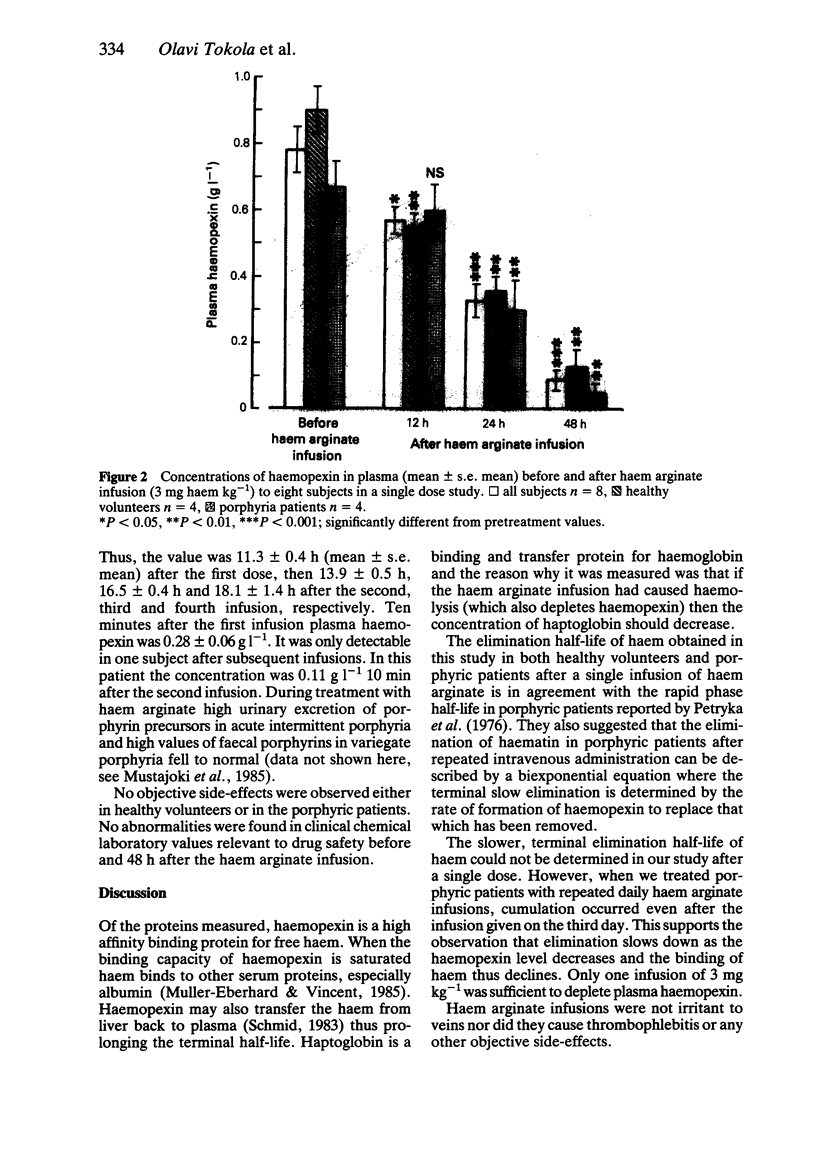
The pharmacokinetics of haem were investigated after intravenous administration of a therapeutic dose of haem arginate (3 mg haem kg-1) to four healthy volunteers and four symptomless porphyric patients. Plasma haem concentrations were measured also during a treatment course of four infusions in six patients with porphyria. Plasma haem concentrations declined monoexponentially over 48 h in both healthy volunteers and porphyric patients, with a mean +/- s.e. mean elimination half-life of 10.8 +/- 0.6 h. Other kinetic parameters were also similar in the two groups, total plasma clearance was 3.7 +/- 0.4 ml min-1 and volume of distribution was 3.37 +/- 0.34 l. In the multiple dose study the elimination half-life increased significantly, from 11.3 +/- 0.4 h to 18.1 +/- 1.4 h over 4 consecutive days. Plasma haemopexin values decreased with time after a single haem arginate dose. The infusion of haem arginate did not cause thrombophlebitis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown R. D., Manno J. E. ESTRIP, a BASIC computer program for obtaining initial polyexponential parameter estimates. J Pharm Sci. 1978 Dec;67(12):1687–1691. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600671214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar G. J., Bossenmaier I., Cardinal R., Petryka Z. J., Watson C. J. Transitory renal failure following rapid administration of a relatively large amount of hematin in a patient with acute intermittent porphyria in clinical remission. Acta Med Scand. 1978;203(5):437–443. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1978.tb14903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar G. J., Bossenmaier I., Petryka Z. J., Cardinal R., Watson C. J. Effects of hematin in hepatic porphyria. Further studies. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jul;83(1):20–30. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-1-20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glueck R., Green D., Cohen I., Ts'ao C. H. Hematin: unique effects of hemostasis. Blood. 1983 Feb;61(2):243–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Riegelman S. Assessment of pharmacokinetic constants from postinfusion blood curves obtained after I.V. infusion. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Jan;59(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl K. E., Moore M. R., Thompson G. G., Goldberg A. Treatment with haematin in acute hepatic porphyria. Q J Med. 1981 Spring;50(198):161–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall D. W. Instability of hematin solutions. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 23;311(8):539–539. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408233110819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. L., Dudley M. D., Pearson R. D. Coagulopathy associated with hematin treatment for acute intermittent porphyria. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Dec;95(6):700–701. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-6-700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Eberhard U., Vincent S. H. Concepts of heme distribution within hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Mar 15;34(6):719–725. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90749-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustajoki P. Prevention and treatment of acute porphyric attacks. Ann Clin Res. 1985;17(6):289–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierach C. A., Bossenmaier I., Cardinal R., Weimer M., Watson C. J. Hematin therapy in porphyric attacks. Klin Wochenschr. 1980 Aug 15;58(16):829–832. doi: 10.1007/BF01491103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R. Hepatic heme metabolism: new aspects and speculations. Semin Liver Dis. 1983 Feb;3(1):83–86. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


