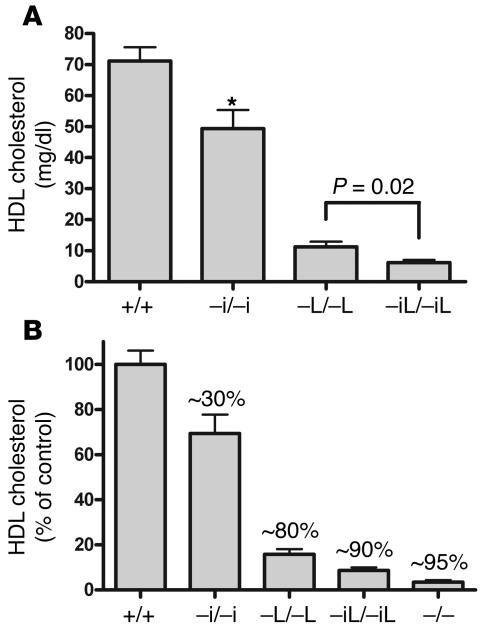
Figure 4. Tissue-specific contributions of ABCA1 to plasma HDL cholesterol levels.
(A) Plasma HDL cholesterol levels in control mice, and mice lacking intestinal ABCA1 (–i/–i), hepatic ABCA1 (–L/–L), or both (–iL/–iL). Mice lacking both hepatic and intestinal ABCA1 had a further significant decrease in plasma HDL cholesterol compared with mice lacking hepatic ABCA1. (B) Plasma HDL cholesterol levels as a percentage of those of strain-matched controls. The percentage decrease compared with strain-matched controls is indicated over each bar. Deletion of hepatic and intestinal ABCA1 results in an approximately 90% decrease in plasma HDL cholesterol, similar to that in mice lacking ABCA1 globally (–/–). n ≥ 4 mice per group. *P < .01.