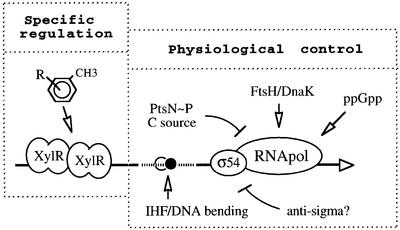
Fig. 3. Integration of specific and physiological signals on the outcome of the Pu promoter of the TOL plasmid pWW0. This archetypal promoter receives both inducer-specific and overall physiological inputs. The specific regulation that makes Pu respond to toluene and xylenes involves only the XylR regulator. On the contrary, metabolic inputs are channeled towards the transcription machinery through multiple molecular assets. These include the control of the activity or the turnover of the σ54 factor in vivo (perhaps through the FtsH/DnaK system, or an antisigma factor or both) (Cases et al., 1996; Carmona and de Lorenzo, 1999), the action of the phosphorylated form of PtsN (Cases et al., 1999) and also the influence of intrinsic or factor (IHF)-mediated DNA bending. The related Po promoter of catabolic plasmid pVI150 (see Figure 2B) seems to react positively to the intracellular levels of the alarmone ppGpp (Sze et al., 1999), whereas the response of Pu to the stringent response is far less pronounced (Carmona et al., 2000).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.