Abstract
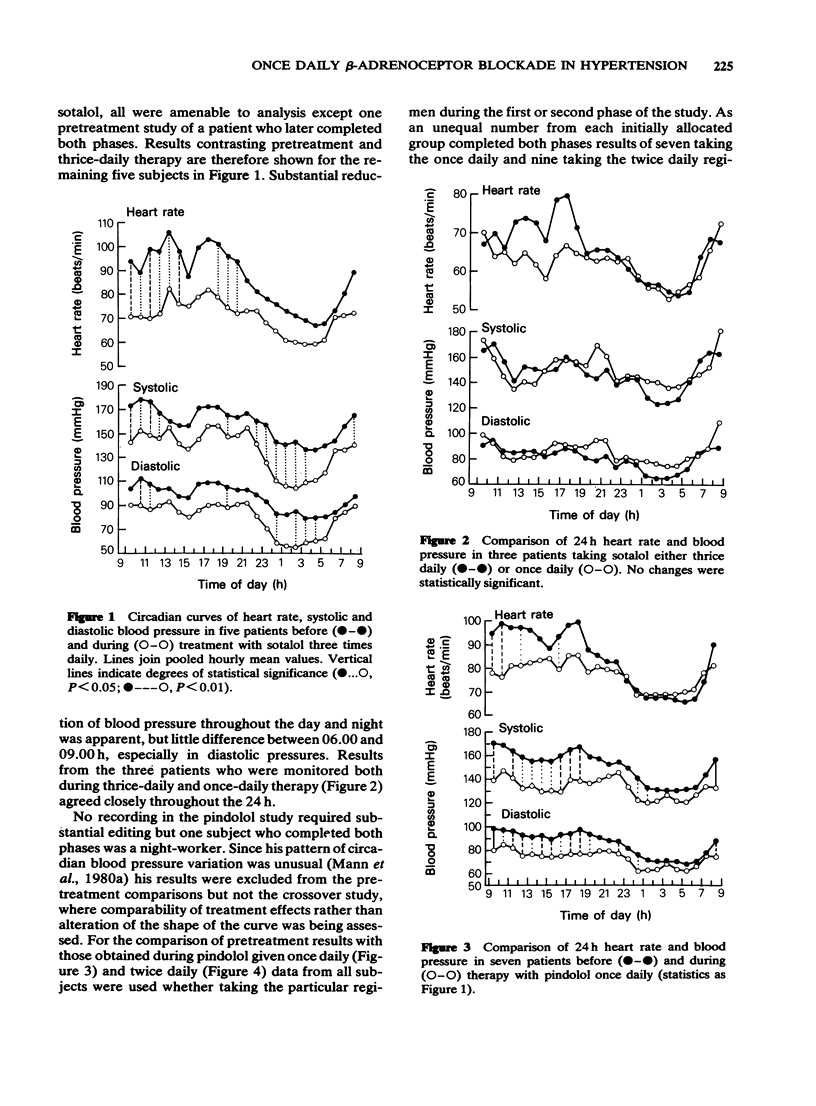
1 The ambulant intra-arterial blood pressure of eighteen hypertensive subjects was monitored before and again after 3 months treatment with thrice daily sotalol (six patients), twice daily pindolol (six patients) and once daily pindolol (six patients). 2 Three patients in the sotalol group underwent a third study having changed to a once daily regimen; similarly six patients in the pindolol groups were restudied having crossed over to the alternative pindolol dosing regimen, total daily dosage being maintained in all cases. 3 Comparison of 24 h blood pressure curves before and after treatment showed effective daytime reduction but less consistent effects at night. 4 In the crossover experiments once daily and multiple daily dosing regimens produced identical patterns of reduction over 24 h in both blood pressure and heart rate. 5 It is inferred that in the treatment of hypertension, once daily dosing with standard preparations of beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents is probable adequate.
Full text
PDF

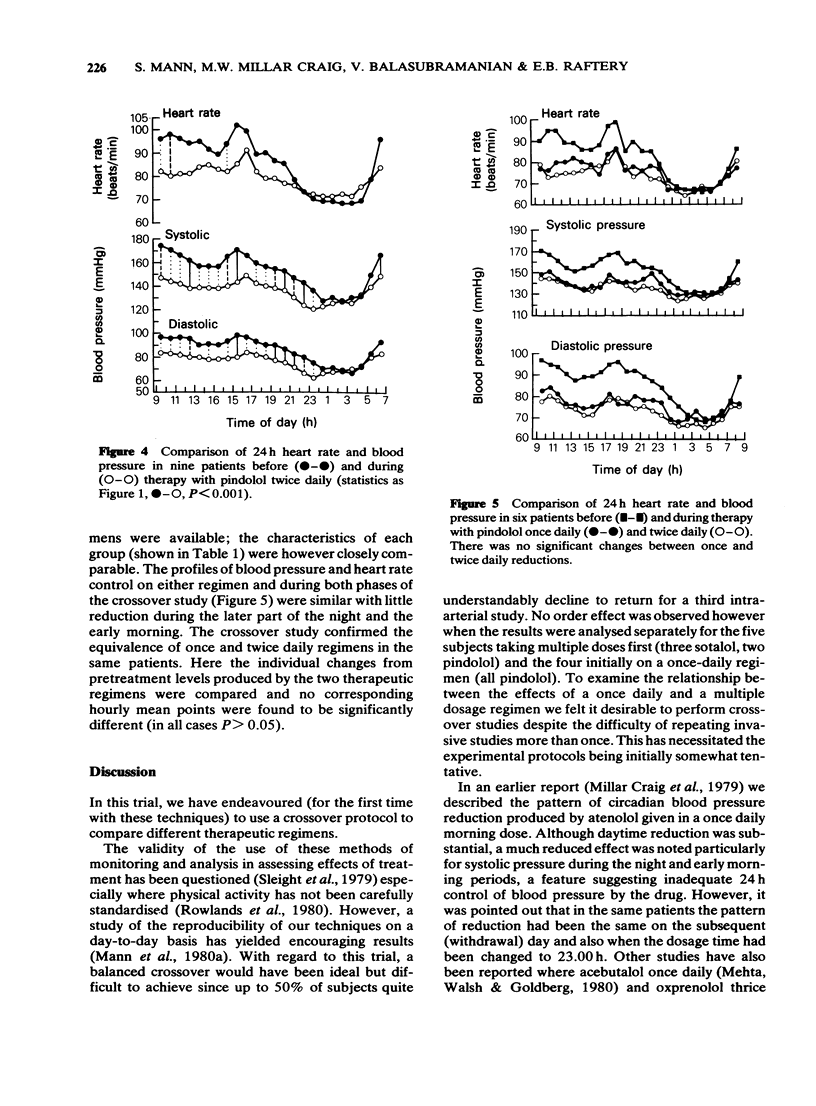


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aellig W. H. beta-Adrenoceptor blocking activity and duration of action of pindolol and propranolol in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;3(2):251–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1976.tb00600.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobik A., Jennings G., Korner P. I. Plasma pindolol levels and their significance in the assessment of cardiac beta blockade. Med J Aust. 1977 Sep 3;2(2 Suppl):3–5. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb113905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. C., Carruthers S. G., Kelly J. G., McDevitt D. G., Shanks R. G. Observations on the efficacy and pharmacokinetics of sotalol after oral administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Mar 22;09(5-6):367–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00606550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashman P. M., Stott F. D., Craig M. W. Hybrid system for fast data reduction of long-term blood-pressure recordings. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1979 Sep;17(5):629–635. doi: 10.1007/BF02440908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig M. W., Kenny D., Mann S., Balasubramanian V., Raftery E. B. Effect of once-daily atenolol on ambulatory blood pressure. Br Med J. 1979 Jan 27;1(6158):237–238. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6158.237-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floras J. S., Fox P., Hassan M. O., Jones J. V., Sleight P., Turner K. L. Assessment of the antihypertensive effect of atenolol with 24 h ambulatory monitoring of blood pressure. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Dec;57 (Suppl 5):387s–389s. doi: 10.1042/cs057387s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatley M. S. To be taken as directed. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1968 Jul;16(1):39–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. D. Initial treatment of the young hypertensive: thiazide diuretic or beta-adrenoreceptor-blocking agent in a single daily dose? Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1976 Dec;3:631s–633s. doi: 10.1042/cs051631s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gugler R., Höbel W., Bodem G., Dengler H. J. The effect of pindolol on exercise-induced cardiac acceleration in relation to plasma levels in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Feb;17(2):127–133. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975172127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S., Craig M. W., Altman D. G., Melville D. I., Raftery E. B. The effects of metoprolol on ambulatory blood pressure. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Dec;57 (Suppl 5):375s–377s. doi: 10.1042/cs057375s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S., Millar Craig M. W., Melville D. I., Cashman P. M., Raftery E. B. An ambulatory trial of guanfacine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980;10 (Suppl 1):103S–107S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb04915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall A., Barritt D. W. Drug complience in hypertensive patients. Br Med J. 1977 May 14;1(6071):1278–1279. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6071.1278-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar Craig M. W., Mann S., Balasubramanian V., Raftery E. B. Blood pressure circadian rhythm in essential hypertension. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1978 Dec;4:391s–393s. doi: 10.1042/cs055391s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar-Craig M. W., Hawes D., Whittington J. New system for recording ambulatory blood pressure in man. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1978 Nov;16(6):727–731. doi: 10.1007/BF02442453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reybrouck T., Amery A., Fagard R., Jousten P., Lijnen P., Meulepas E. Beta-blockers: once or three times a day? Br Med J. 1978 May 27;1(6124):1386–1388. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6124.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. B., Stallard T. J., Watson R. D., Littler W. A. The influence of physical activity on arterial pressure during ambulatory recordings in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Jan;58(1):115–117. doi: 10.1042/cs0580115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMIRK F. H., VEALE A. M., ALSTAD K. S. Basal and supplemental blood pressures in relationship to life expectancy and hypertension symptomatology. N Z Med J. 1959 Dec;58:711–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleight P., Floras J., Jones J. V., Hassan M. O. Effect of once-daily atenolol on ambulatory blood pressure. Br Med J. 1979 Feb 17;1(6161):491–491. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6161.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub Y. M., Rosenfeld J. B. Once-a-day pindolol in hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 May;21(5):588–592. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977215588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. D., Stallard T. J., Littler W. A. Influence of once-daily administration of beta-adrenoceptor antagonists on arterial pressure and its variability. Lancet. 1979 Jun 9;1(8128):1210–1213. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91896-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M., Morgan G., Morgan T. The effect on blood pressure of beta-adrenoreceptor-blocking drugs given once daily. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1976 Dec;3:527s–528s. doi: 10.1042/cs051527s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


