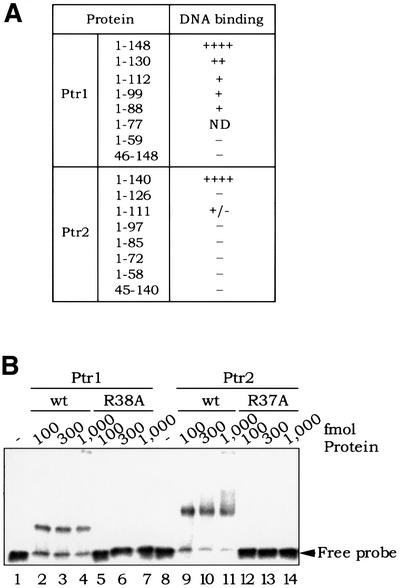
Fig. 7. (A) Deletion analysis of Ptr1 and Ptr2. Ptr1 and Ptr2 variants, lacking either their predicted HTH domains (N-terminal deletions Ptr1[46–148] and Ptr2[45–140]) or C-terminal segments of varying length, were produced in E.coli and purified as described for the wild-type proteins. The ability of each Ptr1 and Ptr2 variant to bind its cognate DNA (site 1-7 for Ptr1, and site 2-13 for Ptr2) was compared with that of the wild-type proteins Ptr1[1–148] and Ptr2[1–140], respectively. The Ptr1[1–77] variant protein could not be obtained in soluble form from overproducing E.coli cells, and was not tested for DNA binding. (B) Analysis of Ptr1 and Ptr2 alanine substitution mutants. DNA binding by Ptr1-R38A (lanes 5–7) and wild-type Ptr1 (lanes 2–4) was compared in a standard EMSA. Similarly, Ptr2-R37A binding to DNA (lanes 12–14) was compared with that of wild-type Ptr2 (lanes 9–11).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.