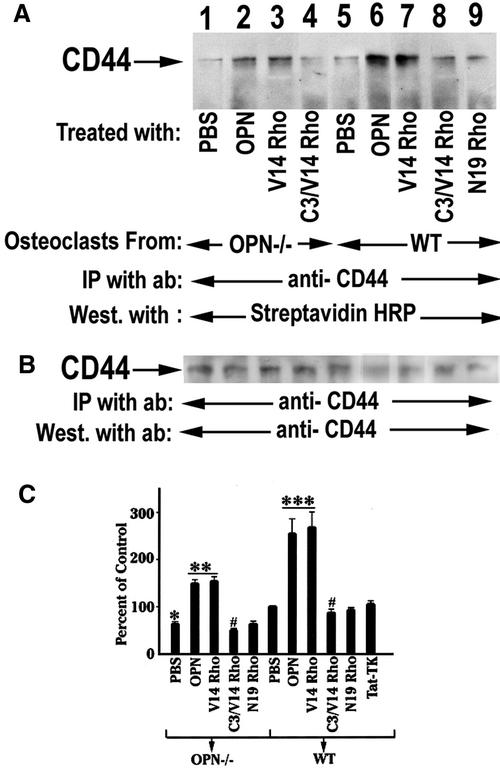
Figure 7.
The effects of OPN or TAT-Rho protein transductions on CD44 surface expression. (A) Osteoclasts isolated from OPN−/− (lanes 1–4) and WT (lanes 5–9) mice were surface labeled with biotin after various treatments as indicated in the figure. The lysates were immunoprecipitated with an antibody to CD44. (A) Immunoprecipitates were blotted with streptavidin-HRP to visualize the surface expression of CD44. (B) The CD44 immunoblot was stripped and immunoblotted with anti-CD44 and anti-rat, HRP-conjugated primary and secondary antibodies, respectively. OPN (lanes 2 and 6) and RhoVal14 transduction increases surface expression of CD44 in both WT and OPN−/− osteoclasts. C3 exoenzyme blocked RhoVal14-induced CD44 surface expression (lanes 4 and 8). (C) Densitometric scans of three experiments expressed as percent control are shown as mean ±. SEM ***p < 0.0001: OPN, V14 Rho vs. PBS of WT osteoclasts; **p < 0.001: OPN, V14Rho vs. PBS of OPN-deficient osteoclast; #p < 0.01: C3/V14 Rho vs. V14 rho of WT and OPN deficient osteoclast; *p < 0.05: PBS of OPN-deficient osteoclasts vs. PBS of WT osteoclasts.