FIGURE 8.
Water-channel and water-water electrostatics profiles within the lumen of AqpZ(His-174:NHδ) and GlpF (a) (for both embedded in POPE bilayers; results for the channels embedded in POPC bilayers are quantitatively similar and therefore not shown). The profiles were obtained from Eq. 9 by considering all water molecules residing within the lumen of the channel at time t and computing the sum of (untruncated) Coulombic interactions with the surrounding monomer (i.e., channel-luminal water interactions) as well as with other water molecules residing within the lumen of the channel (i.e., luminal water-luminal water interactions). The electrostatic energy (E(z)) was assigned to a position z along the channel axis by using the O atom position of that water whose electrostatic interaction was in question. Averaging was over 5000 configurations separated by 5 ps. Averaging over monomers provides the mean electrostatic energy E(z) with variance  . Standard errors (SE) in E(z) are given as
. Standard errors (SE) in E(z) are given as 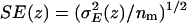 , with nm = 4 being the number of monomers. Origin of z axis was taken as in Fig. 7 b. (b) Water-water correlation for AqpZ(His-174:NHδ) and GlpF. Representative root mean-square deviations from the mean in the correlation profiles are shown for GlpF/POPC and AqpZ/POPC and obtained from the variances among 30, 500-ps-wide time windows. Origin of z axis was taken as in Fig. 7 b. Correlations were only computed within the constriction region according to Eq. 10.
, with nm = 4 being the number of monomers. Origin of z axis was taken as in Fig. 7 b. (b) Water-water correlation for AqpZ(His-174:NHδ) and GlpF. Representative root mean-square deviations from the mean in the correlation profiles are shown for GlpF/POPC and AqpZ/POPC and obtained from the variances among 30, 500-ps-wide time windows. Origin of z axis was taken as in Fig. 7 b. Correlations were only computed within the constriction region according to Eq. 10.

