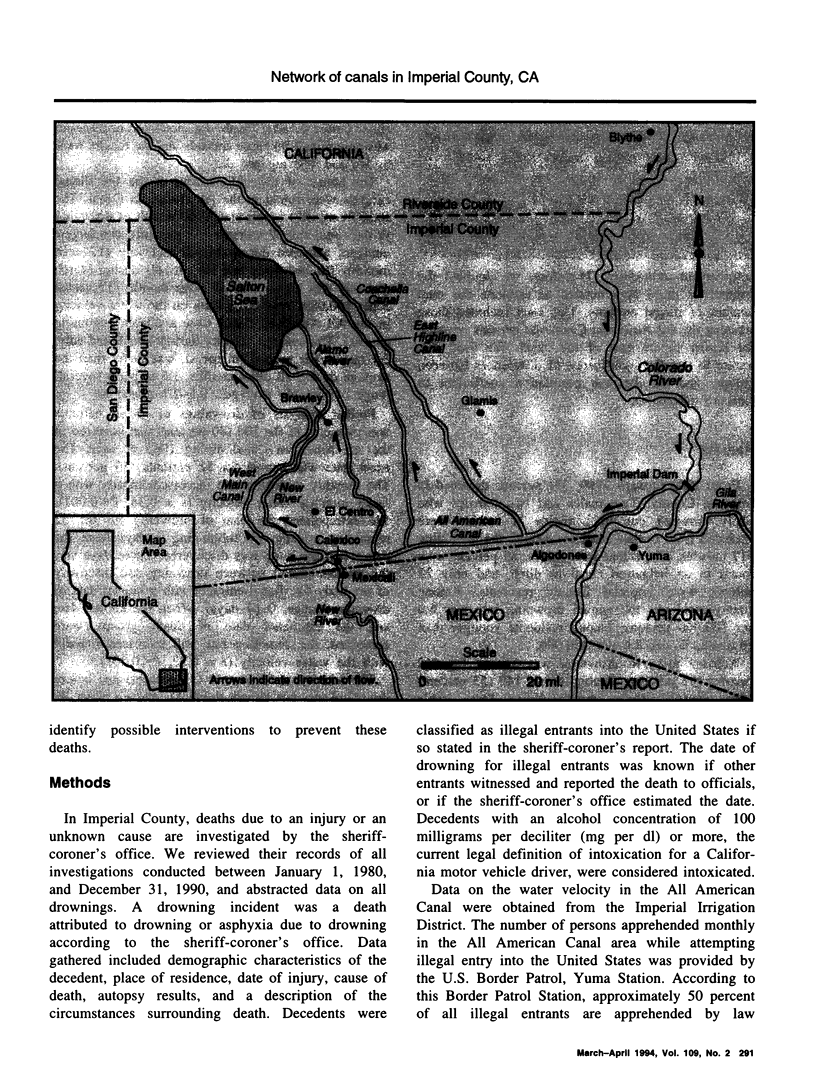
Abstract
Statewide surveillance in California determined that the highest drowning rate from 1980 through 1989 was for the rural, desert county of Imperial (21.9 drownings per 100,000 population). To identify activities associated with drowning in this county, the authors abstracted data from the county sheriff-coroner's reports. From 1980 through 1990, there were 317 unintentional drownings; 85 percent occurred in irrigation canals. The activity prior to drowning was known for 262 persons (83 percent), and the most common activity was illegal entry into the United States. Overall, 140 persons (53 percent) were illegal entrants. Ninety-three percent of illegal entrants drowned in the All American Canal; the monthly drowning rate increased as the monthly average water velocity in the canal increased (r = 0.36; P < 0.001). Forty-eight persons (18 percent) drowned while riding in or on a land vehicle (automobile, pick-up truck, motorcycle, dune buggy, or tractor), the second most common activity associated with drowning. Seventy percent of the 23 drivers had an alcohol concentration of 100 milligrams per deciliter or more, California's limit for intoxication. To reduce drownings in Imperial County, prevention strategies should target persons engaged in at-risk activities near bodies of water. These strategies should include the identification and use of effective canal safety devices.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis S., Ledman J., Kilgore J. Drownings of children and youth in a desert state. West J Med. 1985 Aug;143(2):196–201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearn J. H., Wong R. Y., Brown J., 3rd, Ching Y. C., Bart R., Jr, Hammar S. Drowning and near-drowning involving children: a five-year total population study from the City and County of Honolulu. Am J Public Health. 1979 May;69(5):450–454. doi: 10.2105/ajph.69.5.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan L., Gore E. J., Wentz K., Allen J., Novack A. H. Ten-year study of pediatric drownings and near-drownings in King County, Washington: lessons in injury prevention. Pediatrics. 1989 Jun;83(6):1035–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernez G., Ronfeldt D. The current situation in mexican immigration. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1189–1193. doi: 10.1126/science.251.4998.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintemute G. J., Kraus J. F., Teret S. P., Wright M. A. Death resulting from motor vehicle immersions: the nature of the injuries, personal and environmental contributing factors, and potential interventions. Am J Public Health. 1990 Sep;80(9):1068–1070. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.9.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintemute G. J., Kraus J. F., Teret S. P., Wright M. Drowning in childhood and adolescence: a population-based study. Am J Public Health. 1987 Jul;77(7):830–832. doi: 10.2105/ajph.77.7.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintemute G. J., Teret S. P., Kraus J. F., Wright M. Alcohol and drowning: an analysis of contributing factors and a discussion of criteria for case selection. Accid Anal Prev. 1990 Jun;22(3):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0001-4575(90)90020-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


