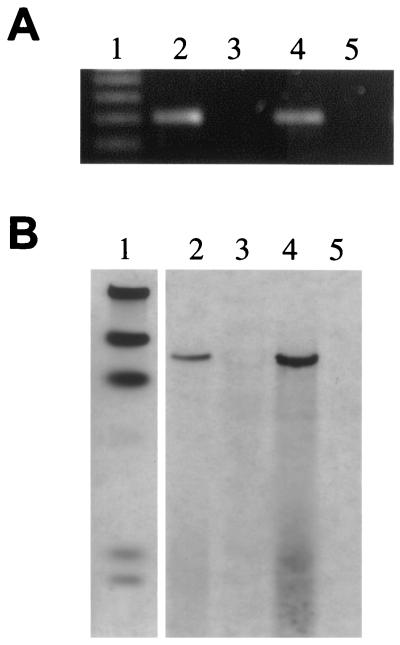
FIG. 1.
PCR and Southern hybridization analysis of a unique DNA fragment show that it is conserved among two M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis isolates tested but not present in M. avium subsp. avium genomic DNA. (A) PCR amplification of specific products representing unique fragment no. 7 from genomic DNA of two representative strains of M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis and two representative isolates of M. avium subsp. avium. Lanes: 1, 100-bp DNA size standards; 2, M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10; 3, M. avium subsp. avium TMC801; 4, M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis ATCC 19698; 5, M. avium subsp. avium deer isolate. (B) Southern hybridization of PstI-restricted genomic DNA (2 μg each) from these same isolates. A DNA fragment amplified with primers designed from the no. 7 sequence was labeled and used as the probe. The data show the presence of this fragment in M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis but not M. avium subsp. avium. The same blot, when stripped and reprobed with the gene encoding the 65-kDa heat shock protein, revealed bands in all four lanes with equal intensities, ruling out the possibility of false-negative hybridizations for the lanes containing M. avium subsp. avium genomic DNA (not shown). The lanes in panel B are identical to those in panel A except that lane 1 contains λ-HindIII size standards.