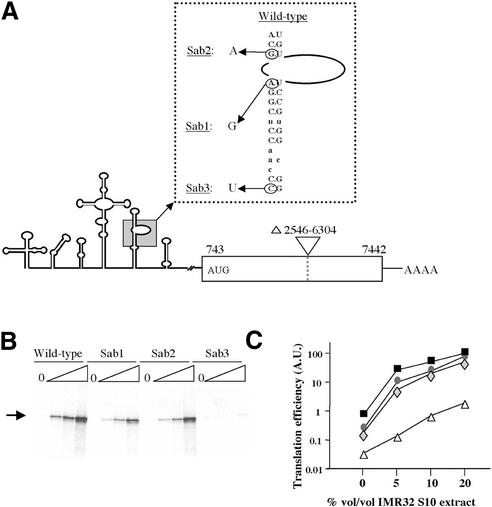
Figure 6.
Translation of mutated PV IRES-carrying mRNAs in ribosome-depleted RRL. (A) Schematic representation of the mutant PV IRES mRNAs. The predicted secondary structure of the PV 5′ UTR is shown. The PV-derived coding region is shown as an open box. Numbers below the coding region refer to the first and last nucleotide of PV sequence. The AUG codon initiating protein synthesis is shown. The natures of the domain V PV IRES mutations (Sab1 at nucleotide 480; Sab2 at nucleotide 481 and Sab3 at nucleotide 469) are indicated in the expanded, boxed inset. (B) Ribosome-depleted translation reactions containing 0, 5, 10 or 20% by volume of IMR 32 cell S10 extract (triangles) and 97 mM and 0.5 mM of KCl and MgCl2, respectively, were programmed with 5 µg/ml (final concentrations) of wild-type or Sab1-3 mutant PV IRES-carrying mRNAs. The position of the authentic PV coding region-derived translation product is indicated. Translation products were analysed as described in the legend to Figure 2. (C) The relative efficiencies of the wild-type and mutant PV IRES to drive translation initiation were calculated with respect to the wild-type mRNA translated in reactions containing 20% of S10 extract (which was arbitrarily taken as 100). The curves represent wild-type (black squares), Sab1 (grey diamonds), Sab2 (grey circles) and Sab3 (open triangles) mRNAs.