Abstract
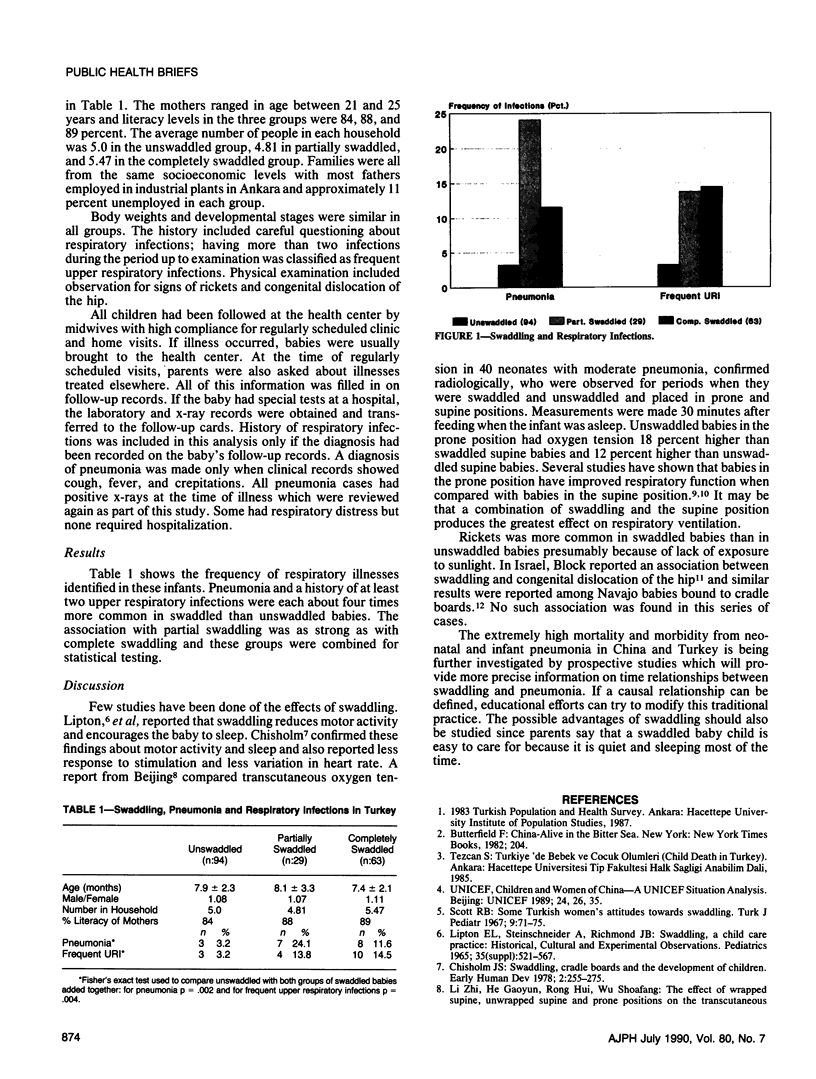
In Turkey and China the ancient practice of swaddling is still commonly practiced. Both countries have extremely high rates of pneumonia, especially during the neonatal period. Preliminary evidence on the possibility that swaddling may interfere with normal respiratory function and thereby predispose to pneumonia was gathered in a teaching health center in Ankara. Babies who had been swaddled for at least three months were four times more likely to have developed pneumonia (confirmed radiologically) and upper respiratory infections than babies who were unswaddled. These preliminary findings were highly significant and are being followed up by further studies.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brackbill Y., Douthitt T. C., West H. Psychophysiologic effects in the neonate of prone versus supine placement. J Pediatr. 1973 Jan;82(1):82–84. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm J. S. Swaddling, cradleboards and the development of children. Early Hum Dev. 1978 Sep;2(3):255–275. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(78)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPTON E. L., STEINSCHNEIDER A., RICHMOND J. B. SWADDLING, A CHILD CARE PRACTICE: HISTORICAL, CULTURAL AND EXPERIMENTAL OBSERVATIONS. Pediatrics. 1965 Mar;35:SUPPL–SUPPL:567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. J., Herrell N., Rubin D., Fanaroff A. Effect of supine and prone positions on arterial oxygen tension in the preterm infant. Pediatrics. 1979 Apr;63(4):528–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. B. Some Turkish women's attitudes towards swaddling. Turk J Pediatr. 1967 Apr;9(2):71–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


