Figure 6.
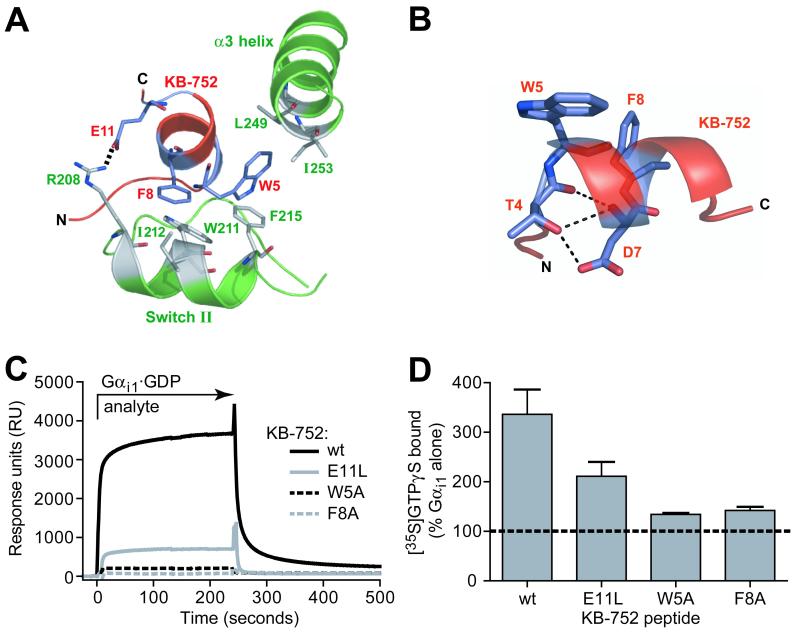
Biochemical confirmation of specific interactions between KB-752 and Gαi1. (A) Positions of KB-752 residues W5, F8, and E11 relative to residues in the switch II and α3 helices of Gαi1. W5 and F8 are placed within hydrophobic pockets formed by Gαi1 residues F215, L249, and I253, and W211, I212, and F215, respectively. E11 forms a salt bridge with R208 of Gαi1. (B) Peptide residues T4 and D7 of the conserved TWXE/DFL binding motif form an intrapeptide hydrogen bond network that helps to orient W5 and F8. (C, D) Effects of W5A, F8A, and E11L mutations to KB-752 activity. (C) Indicated KB-752 mutant or wildtype (wt) peptides were each immobilized to a density of ∼1000 RUs on separate streptavidin-coated flow cells and 50 μM GDP-bound Gαi1 (“analyte”) was injected simultaneously over all four surfaces. (D) Compared to the increase in GTPγS binding observed by addition of 50 μM wildtype KB-752 to 100 nM Gαi1·GDP, substantial reduction of GEF activity is seen upon mutation to the W5, F8, or E11 residue of KB-752.
