Figure 8.
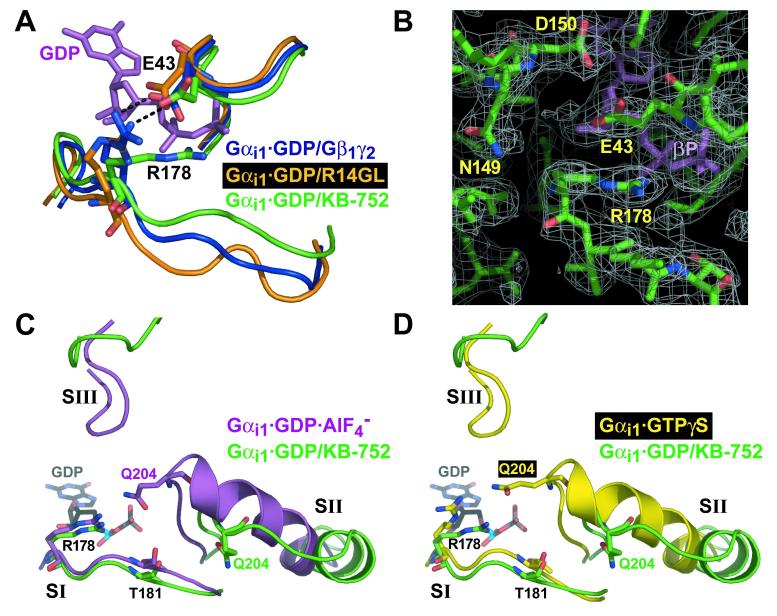
Comparison of switch regions and core catalytic residues of KB-752-bound Gαi1 with other states of Gαi1. (A) Movement of switch I in the Gαi1·GDP/KB-752 complex (green), versus its position in the Gαi1β1γ2 heterotrimer (blue) and the Gαi1·GDP/R14GL complex (orange), results in disruption of a salt-bridge (black dotted line) between R178 and E43 that normally stabilizes bound GDP (magenta) within Gαi1 when complexed to a GDI (Gβγ or GoLoco peptide). (B) Electron density of the R178 side-chain in the Gαi1·GDP/KB-752 complex (from a 2Fo-Fc simulated annealing composite omit map contoured to a level of 1 σ) is denoted by white mesh. In the background is the beta-phosphate of the bound GDP (βP). (C,D) Switch region comparisons with activated Gαi1 states. Switch regions of Gαi1·GDP/KB-752 (green), Gαi1·GDP·AlF4- (PDB code 1GFI; magenta; panel C), and Gαi1·GTPγS (PDB code 1GIA; yellow; panel D), are shown along with the residues critical for GTP hydrolysis (R178 and T181 within switch I and Q204 within switch II). GDP from the Gαi1·GDP/KB-752 structure is shown for reference in each case. Overall conformation of the switch regions of Gαi1·GDP·AlF4- and Gαi1·GTPγS are very similar, save for key changes in the position of catalytic residue side chains (Wall et al., 1998). Whereas switch I of Gαi1·GDP/KB-752 is very similar to that of the activated forms, both switch II and III are dramatically removed from the guanine nucleotide to allow for GDP release. The catalytic Q204 residue within switch II is far removed from the bound nucleotide and active site for GTP hydrolysis in the Gαi1·GDP/KB-752 structure. However, R178 and T181 of switch I are in a strikingly similar position to that of the Gαi1·GDP·AlF4- structure.
