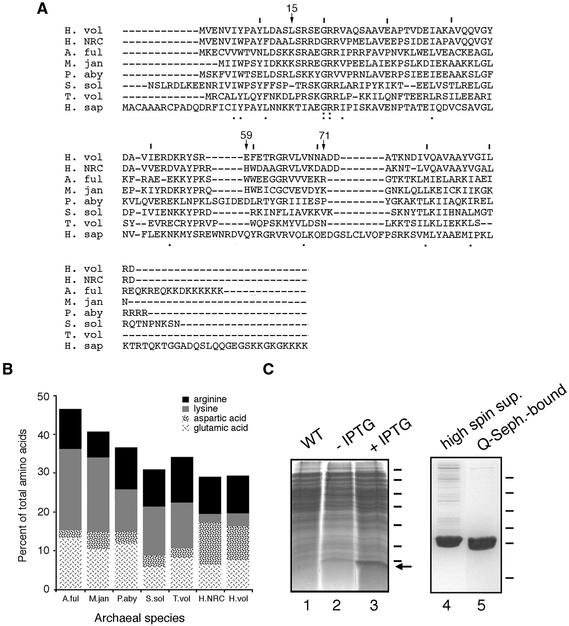
Figure 2.
Purification of H.volcanii SRP19. (A) Alignment of H.volcanii (H. vol) SRP19 with SRP homologs from Halobacterium sp. NRC-1 (H. NRC), Archeoglobus fulgidus (A. ful), Methanococcus jannaschii (M. jan), Pyrococcus abyssi (P. aby), Sulfolobus solfataricus (S. sol), Thermoplasma volcanium (T. vol) and Homo sapiens (H. sap). Lines are placed above every tenth residue in the H.volcanii sequence, while H.volcanii SRP19 residues discussed in the text are denoted by an arrow and the residue number. Homology of the sequences is shown below each residue, with the colon depicting identity and the period depicting similarity. (B) The relative proportions of basic and acidic amino acid residues in archaeal SRP19 proteins are shown. The same species as addressed in (A) are shown. Arginine residues are depicted in black, lysine residues in grey, aspartic acid residues in a speckled pattern and glutamic acid residues in a scratch mark pattern. (C) Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) cells were transformed with pET-Hv19, encoding for H.volcanii SRP19, and induced with 1 mM IPTG for a period of 3 h. Lane 1, wild-type cells; lane 2, uninduced transformed cells; lane 3, induced transformed cells. Molecular weight markers are shown on the right and correspond to 116, 66, 45, 35, 25, 18.4 and 14.4 kDa, while the arrow depicts the position of SRP19. The supernatant of induced cells was applied to Q-Sepharose and eluted with a gradient of NaCl. Lane 4, high spin supernatant; lane 5, Q-Sepharose eluted protein. Molecular weight markers shown on the right correspond to 43, 29, 18.4, 14.4, 6.2 and 3 kDa.