Abstract
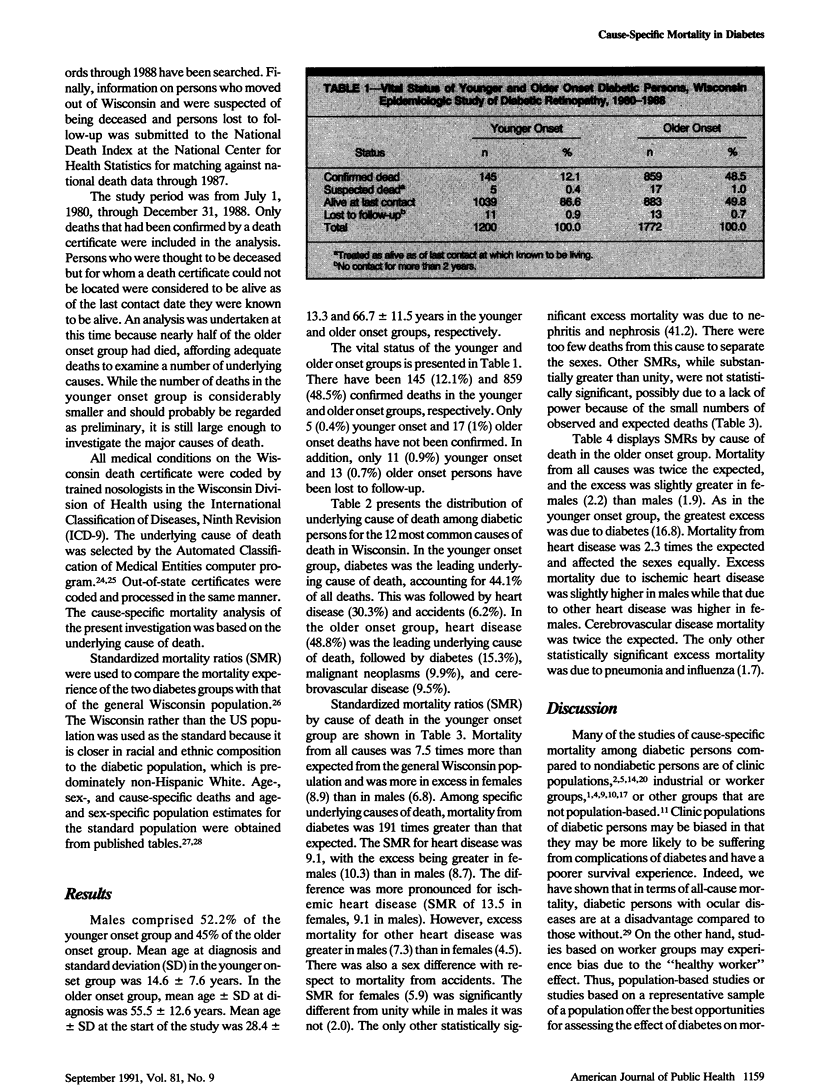
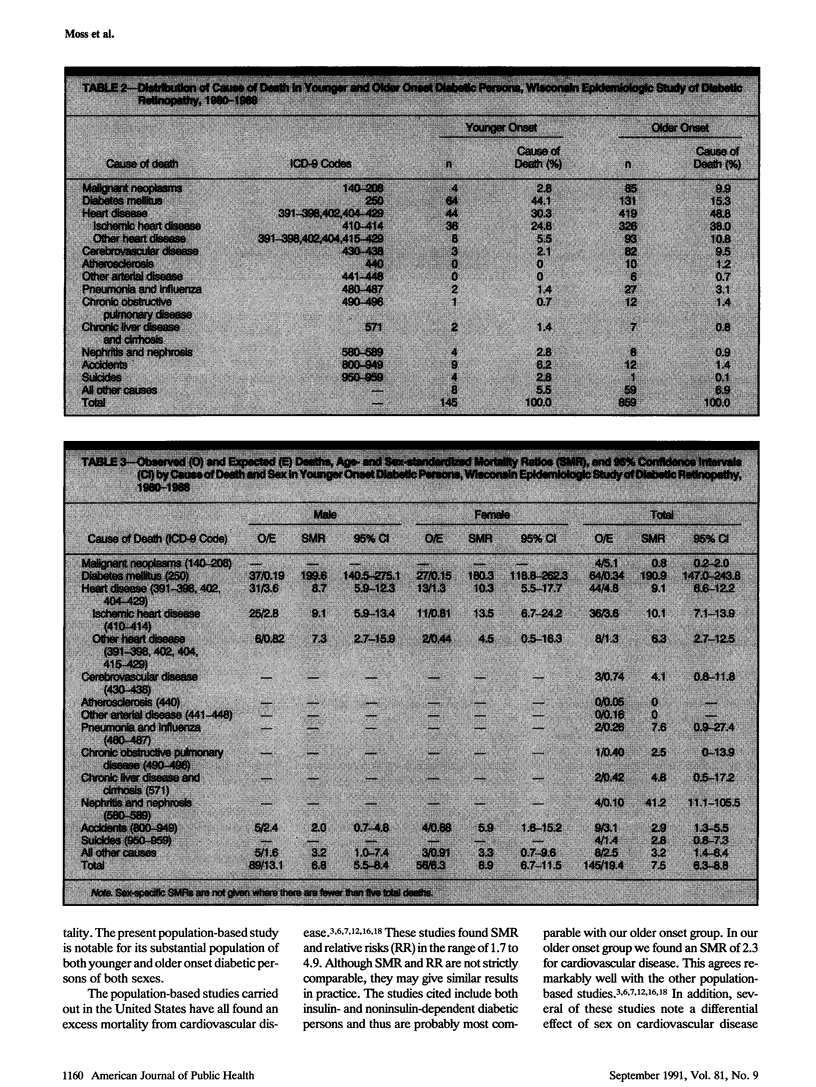
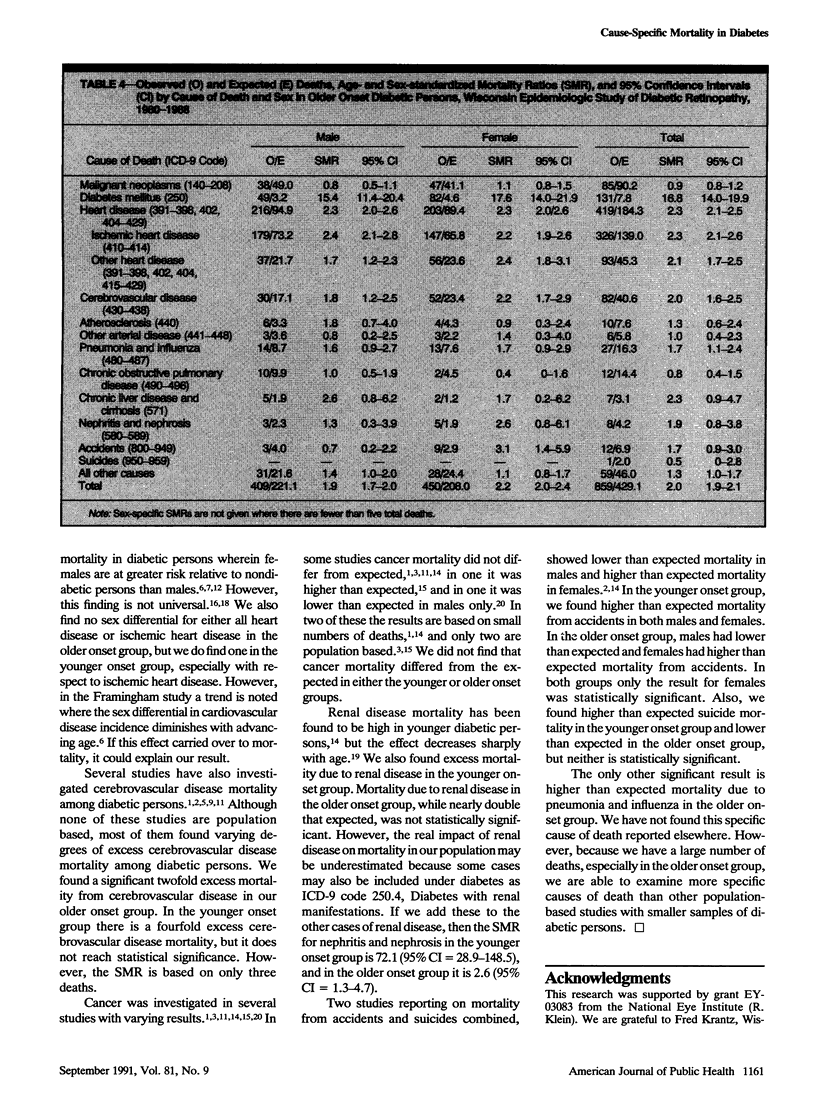
BACKGROUND. Mortality from vascular diseases has been reported to be high in diabetic persons. METHODS. To evaluate mortality from these and other specific causes, we examined cause-specific age-sex standardized mortality ratios in a geographically defined population of younger onset (diagnosed before age 30 and taking insulin, n = 1200) and older onset (diagnosed after age 30, n = 1772) diabetic persons followed for 8.5 years. Cause of death was determined from death certificates. RESULTS. In younger onset persons, age-sex standardized mortality ratios were significantly high (P less than .05) for all causes of death (7.5) as well as for diabetes (191), all heart disease (9.1), ischemic heart disease (10.1), other heart disease (6.3), nephritis and nephrosis (41.2), accidents (2.9), and all other causes (3.2). In older onset persons, age-sex standardized mortality ratios were significantly high for all causes of death (2.0) as well as for diabetes (16.8), all heart disease (2.3), ischemic heart disease (2.3), other heart disease (2.1), stroke (2.0), and pneumonia and influenza (1.7). CONCLUSIONS. Diabetic persons experience very high mortality, especially from vascular diseases, compared to the general population.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett-Connor E., Wingard D. L. Sex differential in ischemic heart disease mortality in diabetics: a prospective population-based study. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Oct;118(4):489–496. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. J., Ostrander L. D., Jr, Carman W. J., Lamphiear D. E. Mortality from coronary heart disease in the Tecumseh study. Long-term effect of diabetes mellitus, glucose tolerance and other risk factors. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Apr;121(4):541–547. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman J. S., Laporte R. E., Kuller L. H., Cruickshanks K. J., Orchard T. J., Wagener D. K., Becker D. J., Cavender D. E., Drash A. L. The Pittsburgh insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) morbidity and mortality study. Mortality results. Diabetes. 1984 Mar;33(3):271–276. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.3.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschwege E., Richard J. L., Thibult N., Ducimetière P., Warnet J. M., Claude J. R., Rosselin G. E. Coronary heart disease mortality in relation with diabetes, blood glucose and plasma insulin levels. The Paris Prospective Study, ten years later. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1985;15:41–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. H., Elford J., Goldblatt P., Adelstein A. M. Diabetes mortality: new light on an underestimated public health problem. Diabetologia. 1983 May;24(5):336–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00251820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. H., Shipley M. J., Rose G., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Mortality from coronary heart disease and stroke in relation to degree of glycaemia: the Whitehall study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Sep 24;287(6396):867–870. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6396.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiss L. S., Herman W. H., Teutsch S. M. Diabetes and renal mortality in the United States. Am J Public Health. 1985 Nov;75(11):1325–1326. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.11.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Hougaard P. Epidemiological studies of diabetes mellitus in Denmark: 5. Mortality and causes of death among insulin-treated diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1984 Mar;26(3):190–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00252405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman J. B., Medalie J. H., Goldbourt U. Differences in cardiovascular morbidity and mortality between previously known and newly diagnosed adult diabetics. Diabetologia. 1977 May;13(3):229–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01219704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyden S., Heiss G., Bartel A. G., Hames C. G. Sex differences in coronary mortality among diabetics in Evans County, Georgia. J Chronic Dis. 1980;33(5):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(80)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., McCartney P., Keen H. The Bedford survey: ten year mortality rates in newly diagnosed diabetics, borderline diabetics and normoglycaemic controls and risk indices for coronary heart disease in borderline diabetics. Diabetologia. 1982 Feb;22(2):79–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00254833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., McGee D. L. Diabetes and glucose tolerance as risk factors for cardiovascular disease: the Framingham study. Diabetes Care. 1979 Mar-Apr;2(2):120–126. doi: 10.2337/diacare.2.2.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler I. I. Cancer mortality among diabetics. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Mar;44(3):673–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler I. I. Mortality experience of diabetic patients. A twenty-six-year follow-up study. Am J Med. 1971 Dec;51(6):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Klein B. E., Moss S. E., Davis M. D., DeMets D. L. The Wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy. II. Prevalence and risk of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is less than 30 years. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984 Apr;102(4):520–526. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1984.01040030398010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Klein B. E., Moss S. E., Davis M. D., DeMets D. L. The Wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy. III. Prevalence and risk of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is 30 or more years. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984 Apr;102(4):527–532. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1984.01040030405011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Klein B. E., Moss S. E., DeMets D. L., Kaufman I., Voss P. S. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in southern Wisconsin. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Jan;119(1):54–61. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Moss S. E., Klein B. E., DeMets D. L. Relation of ocular and systemic factors to survival in diabetes. Arch Intern Med. 1989 Feb;149(2):266–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman J. C., Donahue R. P., Harris M. I., Finucane F. F., Madans J. H., Brock D. B. Mortality among diabetics in a national sample. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 Aug;128(2):389–401. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Królewski A. S., Czyzyk A., Janeczko D., Kopczyński J. Mortality from cardiovascular diseases among diabetics. Diabetologia. 1977 Aug;13(4):345–350. doi: 10.1007/BF01223277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo P. J., Elveback L. R., Chu C. P., Connolly D. C., Kurland L. T. Diabetes mellitus: incidence, prevalence, survivorship, and causes of death in Rochester, Minnesota, 1945-1970. Diabetes. 1976 Jul;25(7):566–573. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.7.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan W. H., Cedres L. B., Liu K., Dyer A., Schoenberger J. A., Shekelle R. B., Stamler R., Smith D., Collette P., Stamler J. Relationship of clinical diabetes and asymptomatic hyperglycemia to risk of coronary heart disease mortality in men and women. Am J Epidemiol. 1986 Mar;123(3):504–516. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pell S., D'Alonzo C. A. Factors associated with long-term survival of diabetics. JAMA. 1970 Dec 7;214(10):1833–1840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reunanen A. Mortality in type 2 diabetes. Ann Clin Res. 1983;15 (Suppl 37):26–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


