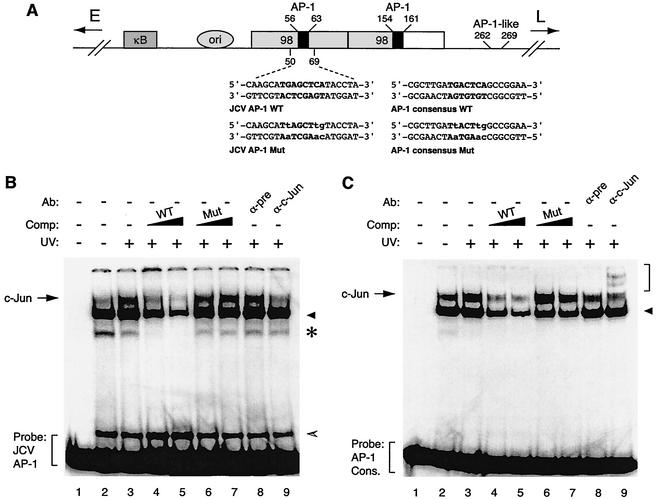
FIG. 1.
c-Jun specifically interacts with the potential c-Jun binding site of JCV in an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. (A) Structural organization of JCV Mad-1 regulatory region. The positions of the NF-κB motif (κB), the origin of viral DNA replication (ori), and the two 98-tandem repeats are depicted. The direction of the expression of early (E) and late (L) genes is indicated by the arrows. Positions of AP-1 binding sequences within JCV regulatory region are also indicated. Wild-type (WT) and mutant (Mut) oligonucleotides used in electrophoretic mobility shift assays as the JCV AP-1 binding site and AP-1 consensus binding site are shown. AP-1 binding sites are in bold, and base substitutions are in lowercase. (B) Competitive band shift and antibody supershift assays. Band shift assays were carried out as described previously (26, 29). A WT JCV AP-1 oligonucleotide spanning nucleotides 50 to 69 of the JCV regulatory region (40,000 cpm/lane) was end labeled and incubated with nuclear extracts (10 μg/lane) prepared from U-87MG cells either untreated (lane 2) or treated with UV light (250 nm, 40 J/m2) (lane 3). In addition, probe plus nuclear extract from UV-treated cells was also incubated with either unlabeled JCV AP-1 WT (lanes 4 and 5) or its mutant (lanes 6 and 7) variant competitor (25- and 150-fold molar excesses, respectively). Probe plus nuclear extract mixture was also incubated either with a preimmune (2 μg) (pre, lane 8) or an anti-c-Jun (KM-1, 2 μg; Santa Cruz) (lane 9) antibody. DNA-protein complexes were then resolved on a 6% polyacrylamide gel under native conditions and visualized by autoradiography as described previously (25, 26). (C) Interaction of c-Jun with AP-1 consensus (cons.) sequence in an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Conditions were as described for panel B except that competitor WT and mutant oligonucleotides are shown as AP-1 consensus WT and AP-1 consensus Mut, respectively, in panel A. In panels B and C, the specific DNA-protein complexes are indicated by an arrow, and nonspecific complexes, where applicable, are indicated by either a solid arrowhead, a hatched arrowhead, or an asterisk. In panel C, a bracket indicates antibody supershifted complexes. Comp., competitor; Ab, antibody.