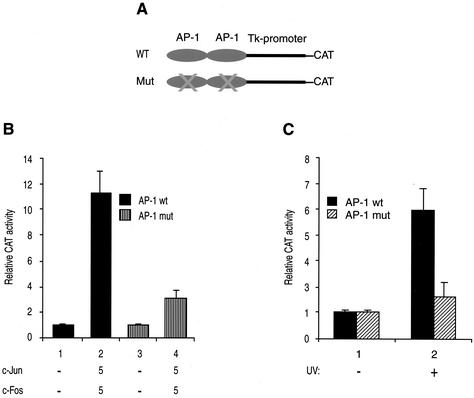
FIG. 3.
AP-1 binding site of JCV confers responsiveness to c-Jun and c-Fos in a heterologous promoter. (A) Schematic representation of a heterologous promoter (pBLCAT2) (8) containing either WT JCV or mutant AP-1 binding sites. A tandem repeat of an oligonucleotide spanning nucleotides 50 to 69 of the JCV Mad-1 regulatory region and containing either WT JCV AP-1 binding site or its mutant variant was cloned upstream of the promoter at BamHI/HindIII sites. The sequences of cloned oligonucleotides for both WT JCV AP-1 oligonucleotide and its mutant variant are shown in Fig. 1A. (B) Induction of transcription by c-Jun and c-Fos. Both the WT and mutant reporter constructs (5 μg) shown in panel A were transfected, as described for Fig. 2A, into U-87MG cells alone or in combination with expression plasmids for c-Jun (RSV-c-Jun; 5 μg) or c-Fos (RSV-c-Fos; 5 μg), and transfectants were then processed as described for Fig. 2A. (C) JCV AP-1 binding sites are responsive to UV induction. Both the WT and mutant reporter constructs (5 μg) shown in panel A were also transfected into U-87MG cells as described for panel B, and transfectants were then either untreated or treated with UV and processed for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity as described for Fig. 2A.