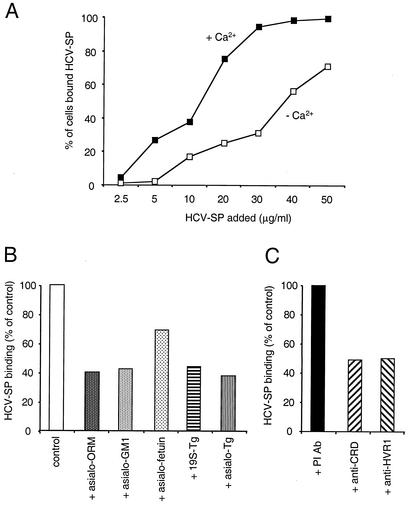
FIG. 5.
HCV-SP binding to HepG2 cells is inhibited by ligands of ASGP-R. (A) HCV-SP binding to HepG2 cells is calcium dependent. Cells and HCV-SP were suspended either in binding buffer in the presence of CaCl2 (▪) or in binding buffer containing 5 mM EGTA in the absence of CaCl2 (□), and a binding assay was performed as in Fig. 2. (B) Effect of ASGP-R ligands on HCV-SP binding in HepG2 cells. Cells were preincubated in binding buffer (with CaCl2) at 4°C either with buffer alone (control), with 5 mg of asialo-orosomucoid (asialo-ORM)/ml, with 200 μg of asialoganglioside (asialo-GM1)/ml, with 2 mg of asialofetuin/ml, with 1 mg of 19S-Tg/ml, or with 0.4 mg of asialo-19S-Tg/ml (asialo-Tg); an HCV-SP binding assay was then performed. (C) Effect of antibodies on HCV-SP binding in HepG2 cells. Cells were preincubated in binding buffer at 4°C with preimmune antibody (PI Ab; 1/100), polyclonal antibody recognizing a peptide in the CRD of ASGP-R (anti-CRD; 1/100), or antibody directed against HVR1 of the E2 envelope protein (anti-HVR1; 1/100); an HCV-SP binding assay was then performed with anti-E1 antibody.